News and publications
publications
The below publications include a funding acknowledgement to the project. PREMSTEM researchers are highlighted as bold. Check out our research highlights page to find summaries of selected papers.
List of publications
A Novel Model for Simultaneous Evaluation of Hyperoxia-Mediated Brain and Lung Injury in Neonatal Rats
Stefanie Obst, Meray Serdar, Josephine Herz, Karina Kempe, Meriem Assili, Mandana Rizazad, Dharmesh Hirani, Miguel A. Alejandre Alcazar, Stefanie Endesfelder, Marius A. Möbius, Mario Rüdiger, Ursula Felderhoff-Müser and Ivo Bendix
Cells 2025, 14(6), 443; https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14060443
Received: 12 February 2025 / Revised: 10 March 2025 / Accepted: 13 March 2025 / Published: 16 March 2025
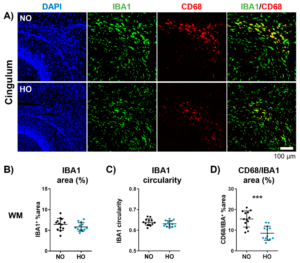
Despite improved neonatal intensive care, the risk of preterm-born infants developing bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) and encephalopathy of prematurity (EoP) remains high. With hyperoxia being a major underlying factor, both preterm-birth-related complications are suggested to be closely interrelated. However, experimental models are lacking for the assessment of the potentially close interplay between the lungs and the brain. In this study, the researchers provide a novel experimental model in neonatal rats to investigate mechanisms potentially linking both organ injuries but also to evaluate novel therapeutic approaches.
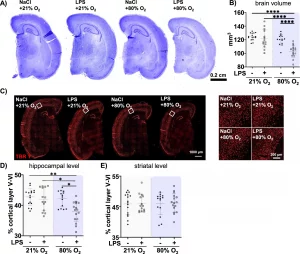
Prenatal inflammation exacerbates hyperoxia-induced neonatal brain injury
Meray Serdar, Kay-Anja Walther, Markus Gallert, Karina Kempe, Stefanie Obst, Nicole Labusek, Ralf Herrmann, Josephine Herz, Ursula Felderhoff-Müser and Ivo Bendix
J Neuroinflammation 2025, 22, 57; https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-025-03389-4
Received: 25 November 2024 / Accepted: 20 February 2025 / Published: 28 February 2025
Preterm-born infants are at high risk to develop white matter injury (WMI). Hyperoxia and perinatal inflammation are main risk factors for preterm birth and associated brain injury. To date, the majority of experimental studies have focused on isolated insults. However, clinically, WMI injury is a multifactorial disorder caused by a variety of triggers. To establish a clinically relevant rodent model of WMI, the researchers combined prenatal inflammation with postnatal hyperoxia to investigate individual, and additive or synergistic effects, on inflammatory processes, myelination and grey matter development.
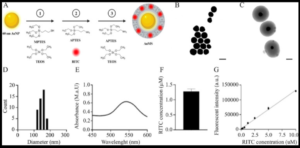
Gold Mesoporous Silica-Coated Nanoparticles for Quantifying and Qualifying Mesenchymal Stem Cell Distribution; a Proof-of-Concept Study in Large Animals
Lotte C C Smeets, Ezgi Sengun, Chloe Trayford, Bram van Cranenbroek, Marien I de Jonge, Katiuscia Dallaglio, Matthias C Hütten, Mark Schoberer, Daan R M G Ophelders, Tim G A M Wolfs, Renate G van der Molen and Sabine van Rijt
ACS Applied Bio Materials 2025, 8 (2), 1511-1523; https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.4c01714
Received: 14 November 2024 / Revised: 21 January 2025 / Accepted: 23 January 2025 / Published: 3 February 2025
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have demonstrated promising therapeutic potential across a wide range of diseases including (multi) organ injury in neonates. Despite the reported preclinical successes of MSC therapy, a major challenge in their clinical translation is a limited understanding of their biodistribution after administration. This knowledge gap needs to be addressed to allow clinical implementation. In this study, the researchers propose that silica-coated gold nanoparticles (AuMS) are a promising tool for in vivo MSC tracing.
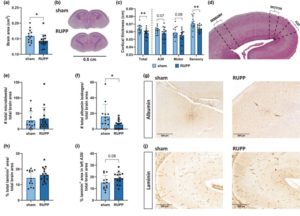
Organ development in growth-restricted fetuses in the
reduced uterine perfusion pressure rat model: A vascular
approach of brain, heart, and kidney
J. Alhama-Riba, C. M. van Kammen, K. T. Nijholt, D. Viveen, K. Amarouchi, D. Shasha, M. M. Krebber, F. E. Hoebeek, A. T. Lely, C. H. A. Nijboer and F. Terstappen
Physiol Rep 2025, Feb 12;13(3):e70244; https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.70244
Received: 16 October 2024 / Revised: 13 January 2025 / Accepted: 31 January 2025
Foetal growth restriction (FGR) increases the risk of developing cardiovascular, renal, and neurovascular diseases. An overlapping vascular pathophysiology as a response to chronic hypoxia and circulatory redistribution in utero, might underlie this lifelong burden. This study aims to assess potential vascular detoriations in multiple organs following FGR using the Reduced Uterine Perfusion Pressure (RUPP) rat model.
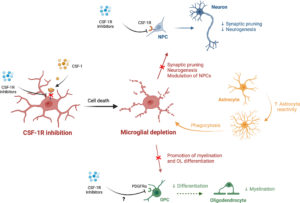
Microglial Depletion, a New Tool in Neuroinflammatory Disorders: Comparison of Pharmacological Inhibitors of the CSF‐1R
David Guenoun, Nathan Blaise, Alexandre Sellam, Julie Roupret‐Serzec, Alice Jacquens, Juliette Van Steenwinckel, Pierre Gressens and Cindy Bokobza
Glia 2024, Dec 24; 73 (4): 686–700; https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.24664
Received: 4 July 2024 / Revised: 6 December 2024 / Accepted: 11 December 2024 / Available online: 24 December 2024
In this review, the researchers focus on the comparison of three different pharmacological CSF-1R inhibitors (PLX3397, PLX5622, and GW2580) regarding microglial depletion. They also highlight the promising results obtained by microglial depletion strategies in adult models of neurological disorders and argue they could also prove promising in neurodevelopmental diseases associated with microglial activation and neuroinflammation. Finally, they discuss the lack of knowledge about the effects of these strategies on neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes in adults and during neurodevelopment.
C-section and systemic inflammation synergize to disrupt the neonatal gut microbiota and brain development in a model of prematurity
Cécile Morin, Flora Faure, Julie Mollet, David Guenoun, Ariane Heydari-Olya, Irvin Sautet, Sihao Diao, Valérie Faivre, Julien Pansiot, Lara Tabet, Jennifer Hua, Leslie Schwendimann, Amazigh Mokhtari, Rebeca Martin-Rosique, Sead Chadi, Mireille Laforge, Charlie Demené, Andrée Delahaye-Duriez, Rochellys Diaz-Heijtz, Bobbi Fleiss, Boris Matrot, Sandrine Auger, Mickael Tanter, Juliette Van Steenwinckel, Pierre Gressens and Cindy Bokobza
Brain, Behavior, and Immunity 2025, 123, 824-837: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2024.10.023
Received: 31 October 2023 / Revised: 7 October 2024 / Accepted: 20 October 2024 / Available online: 22 October 2024
In this research, the team used a model of encephalopathy of prematurity to combine C-section and neonatal systemic inflammation and determine the impact of each factor or their combination on the gut microbiota, microglia activation, myelination, brain connectivity, and behaviour relative to the control condition of vaginal delivery and neonatal systemic saline. In this model, they showed that C-section worsened the effects of neonatal systemic inflammation. The combined impact reduced gut microbial diversity and raised circulating peptidoglycan levels, and C-section intensified microglial/macrophage reactivity and impaired myelination. This synergy between C-section and inflammation also weakened brain functional connectivity. These conditions in preterm infants are linked to heightened neurodevelopmental disorder risks.
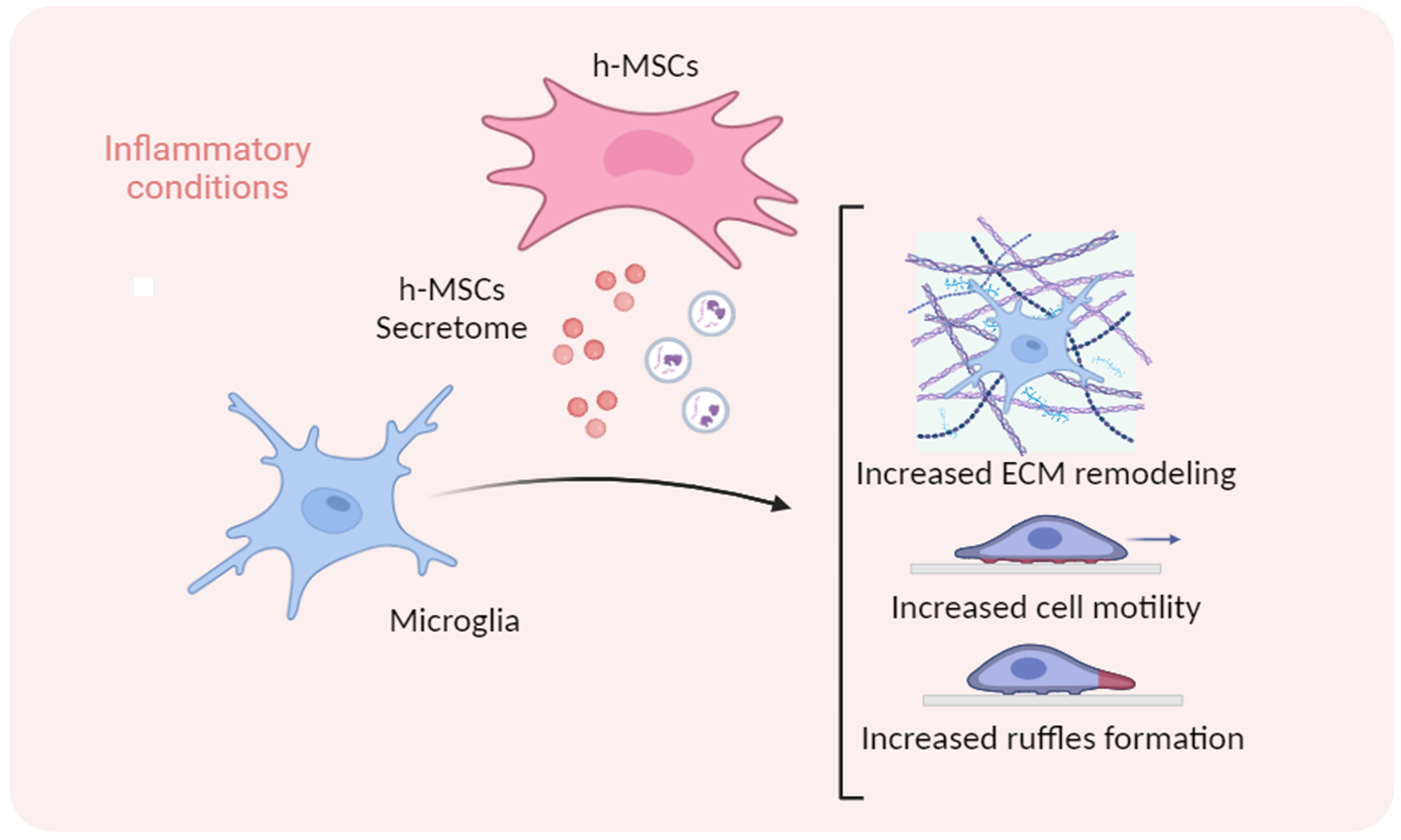
Human Umbilical Cord-Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Extracellular Matrix Remodeling in Microglia
Marta Tiffany Lombardo, Martina Gabrielli, Florence Julien-Marsollier, Valérie Faivre, Tifenn Le Charpentier, Cindy Bokobza, Deborah D’Aliberti, Nicola Pelizzi, Camilla Halimi, Silvia Spinelli, Juliette Van Steenwinckel, Elisabetta A. M. Verderio, Pierre Gressens, Rocco Piazza and Claudia Verderio
Cells 2024, 13 (19), 1665: https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13191665
Received: 13 September 2024 / Revised: 2 October 2024 / Accepted: 5 October 2024 / Published: 9 October 2024
Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate the immune response and are good candidates for cell therapy in neuroinflammatory brain disorders affecting both adult and premature infants. Using an in vitro coculture approach combined with transcriptomic analysis, the research team identified the extracellular matrix as the most relevant pathway altered by the human mesenchymal stem cell secretome in the response of microglia to inflammatory cytokines. They confirmed extracellular matrix remodelling in microglia exposed to the mesenchymal stem cell secretome via immunofluorescence analysis of the matrix component fibronectin and the extracellular crosslinking enzyme transglutaminase-2. Furthermore, an analysis of hallmark microglial functions revealed that changes in the extracellular matrix enhance ruffle formation by microglia and cell motility.
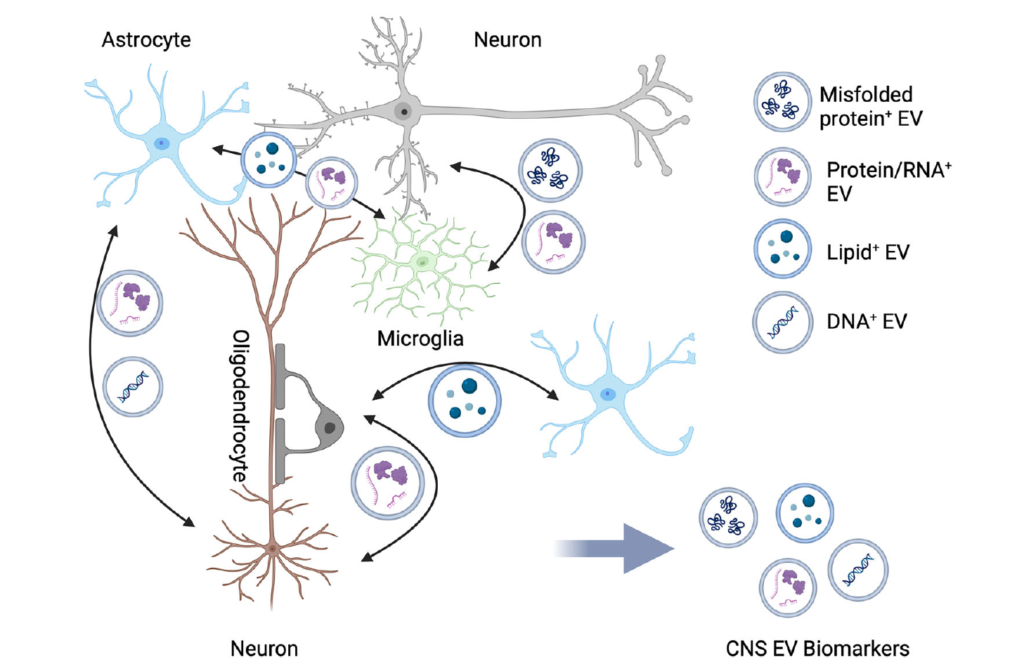
Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Neuron–Glia Communications in the Central Nervous System
Tsuneya Ikezu, Yongjie Yang, Claudia Verderio and Eva-Maria Krämer-Albers
Journal of Neuroscience 2024, 44 (40) e1170242024; https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1170-24.2024
Received: 19 June 2024 / Revised 17 July 2024 / Accepted: 24 July 2024 / Published: 2 October 2024
This review highlights recent breakthroughs in the research of signalling mechanisms between glia and neurons mediated by extracellular vesicles that are important for neural development, axonal maintenance, synaptic functions, and disease progression in the mammalian nervous system. The researchers discuss the biological roles of extracellular vesicles released from neurons, astroglia, microglia, and oligodendroglia in the nervous system and their implications in neurodegenerative disorders.
Neonatal inflammation impairs developmentally-associated microglia and promotes a highly reactive microglial subset
Adrien Dufour, Ariane Heydari Olya, Sophie Foulon, Clémence Réda, Amazigh Mokhtari, Valérie Faivre, Jennifer Hua, Cindy Bokobza, Andrew D. Griffiths, Philippe Nghe, Pierre Gressens and Andrée Delahaye-Duriez, Juliette Van Steenwinckel
Brain, Behavior, and Immunity 2025 Volume 123, Pages 466-482: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2024.09.019
Received: 13 May 2024 / Revised: 10 September 2024 / Accepted: 13 September 2024 / Available online: 23 September 2024
Using whole and targeted single cell RNA-sequencing of brain myeloid cells and flow cytometry in a mouse model of neurodevelopmental disorder induced by neonatal inflammation, this study highlighted major changes in brain myeloid cells and microglial subsets developmental trajectories, including an infiltration of neutrophils in the brain; the emergence of a specific subset of microglia expressing the complement receptor C5AR1 in which inflammatory pathways are strongly overexpressed; and a reduction of major microglial subsets including Spp1-microglia supporting oligodendrocyte differentiation, primitive and proliferative microglia.
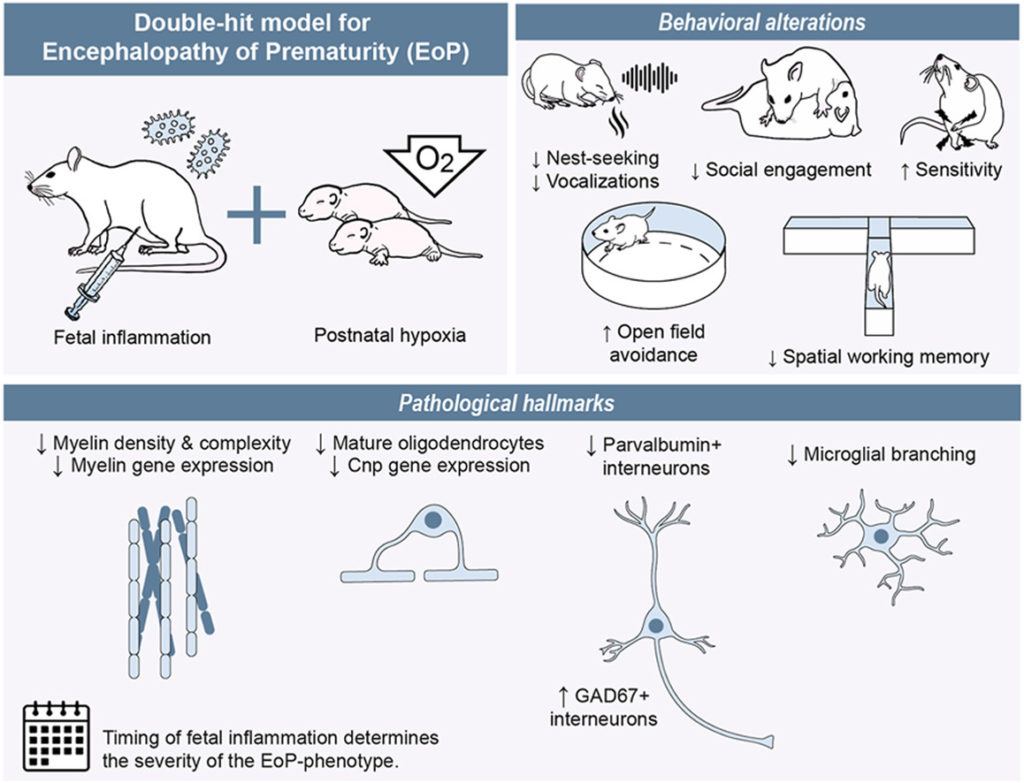
Timed fetal inflammation and postnatal hypoxia cause cortical white matter injury, interneuron imbalances, and behavioral deficits in a double-hit rat model of encephalopathy of prematurity
M.J.V. Brandt, C.M. Kosmeijer, E.J.M. Achterberg, C.G.M. de Theije, C.H. Nijboer
Brain, Behavior, & Immunity – Health 2024 Volume 40: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbih.2024.100817
Received: 29 June 2024 / Accepted: 4 July 2024 / Available online: 5 July 2024
This article explores a double-hit rat model that can be used to investigate pathophysiological mechanisms and potential therapies for encephalopathy of prematurity (EoP). Rats exposed to foetal inflammation and postnatal hypoxia showed neurodevelopmental impairments, such as reduced nest-seeking ability, ultrasonic vocalisations, social engagement and working memory, and increased anxiety and sensitivity. Impairments in myelination, oligodendrocyte maturation and interneuron development were examined as hallmarks for EoP, in different layers and coordinates of the cortex using histological and molecular techniques.
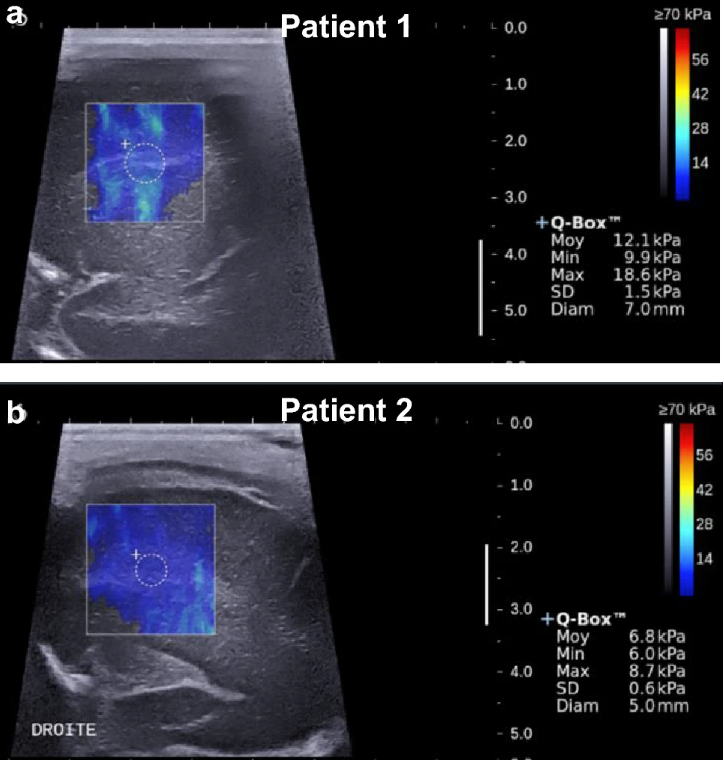
Transfontanellar shear wave elastography of the neonatal brain for quantitative evaluation of white matter damage
Flora Faure, Marianne Alison, Mariantonietta Francavilla, Priscilla Boizeau, Sophie Guilmin Crepon, Chung Lim, Gregory Planchette, Mickael Prigent, Alice Frérot, Mickael Tanter, Charlie Demené, Olivier Baud and Valérie Biran
Sci Rep 2024 14, 11827: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-60968-w
Received: 3 November 2023 / Accepted: 29 April 2024 / Published: 23 May 2024
Cerebral white matter damage is the most frequent brain lesion seen in infants surviving preterm birth. Qualitative B-mode cranial ultrasound is widely used to assess brain integrity at the bedside but has its limitations in predicting long-term outcomes compared to magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Shear wave elastography is a promising ultrasound imaging modality that might improve this limitation by detecting quantitative differences in tissue stiffness. Measuring tissue stiffness could be a useful screening method for the early identification of preterm infants at high risk of white matter damage.
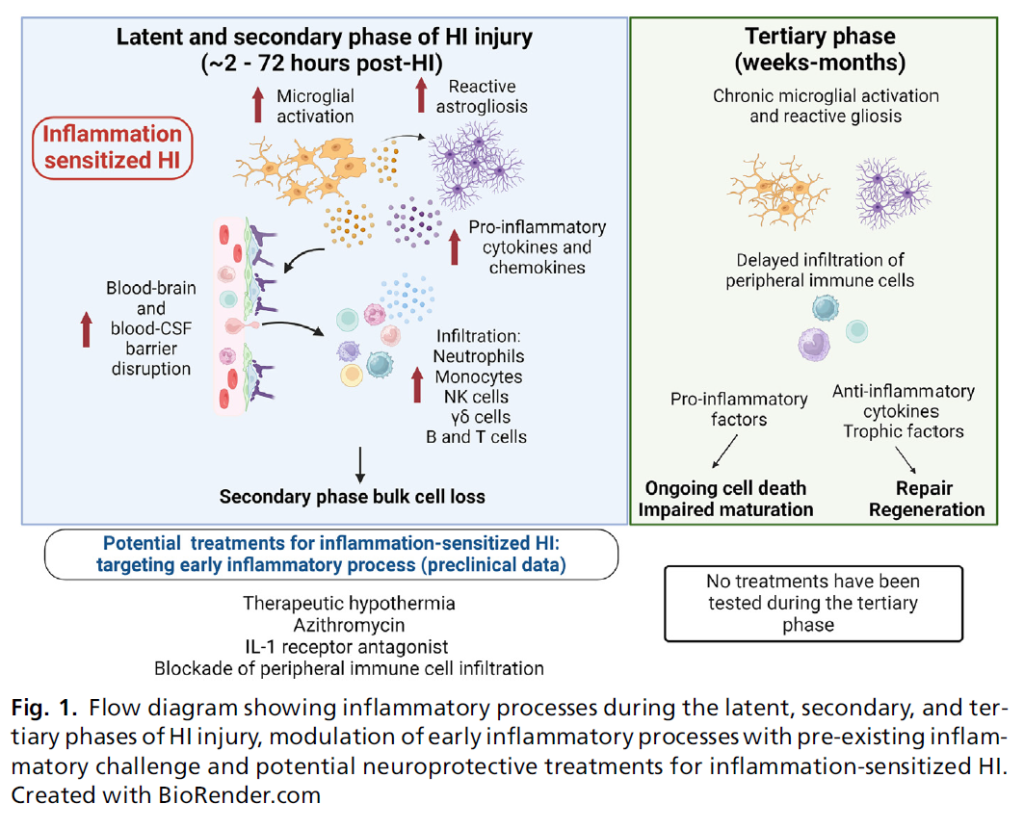
Uncovering the Role of Inflammation with Asphyxia in the Newborn
Simerdeep K. Dhillon, Pierre Gressens, John Barks and Alistair J. Gunn
Clin Perinatol 51 2024, 551–564: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clp.2024.04.012
Available online: 22 May 2024
This review discusses the role of acute and chronic inflammation in mediating neural injury after hypoxia-ischemia (HI), modification of neuro-inflammatory responses with a combination of HI and inflammatory insults and potential interventions.
Download PDF of Uncovering the role of inflammation with asphyxia in the newborn
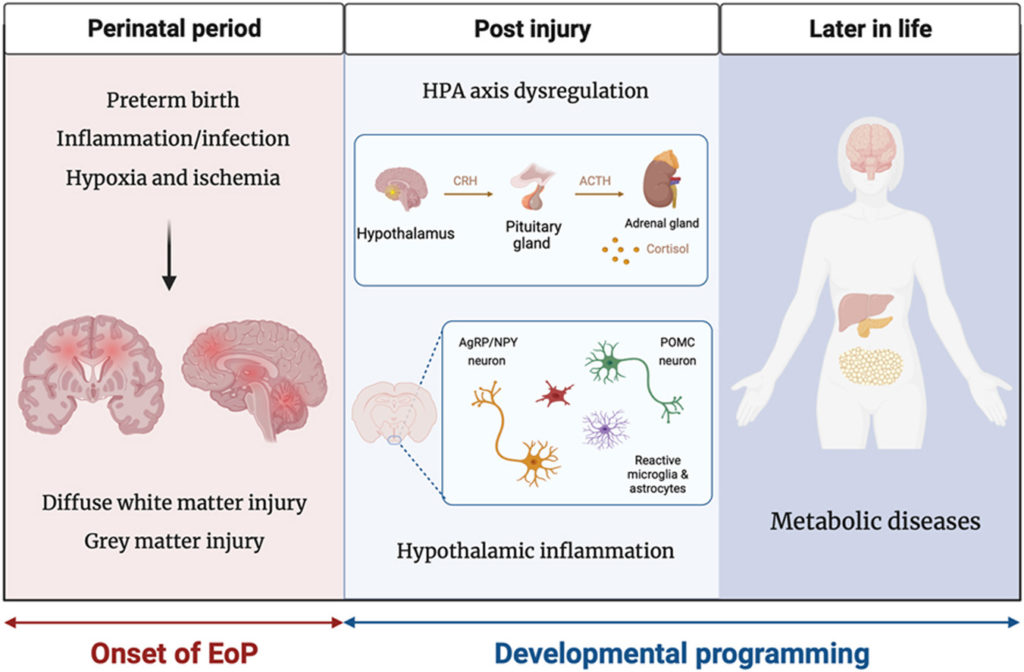
Preterm birth: A neuroinflammatory origin for metabolic diseases?
Sihao Diao, Chao Chen, Alexandre Benani, Christophe Magnan, Juliette Van Steenwinckel, Pierre Gressens, Céline Cruciani-Guglielmacci, Alice Jacquens and Cindy Bokobza
Brain, Behavior, & Immunity – Health 2024, Volume 37: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbih.2024.100745
Received: 28 August 2023 / Revised: 16 January 2024 / Accepted: 21 February 2024 / Published: 7 March 2024
In this article the researchers review epidemiological evidence that links preterm birth to metabolic diseases and discuss possible synergic roles of preterm birth and neuroinflammation from encephalopathy of prematurity in the development of metabolic diseases. They also explore theoretical underlying mechanisms regarding developmental programming of the energy control system and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis.
A Neonatal Rodent Model of Retroorbital Vein Injection
Eridan Rocha-Ferreira, Syam Nair, Owen Herrock, Erik Axel Andersson, Carl Joakim Ek, Carina Mallard and Henrik Hagberg
J. Vis. Exp. 2024, (204), e65386; https://doi.org/10.3791/65386
Published: 23 February 2024
The protocol aims to demonstrate a reproducible venous administration route that can be used in rats and mice throughout the neonatal period. This procedure is important for preclinical rodent studies that wish to mirror drug administration in neonatal care units primarily using intravenous administration.
Quantification of brain-wide vascular resistivity via ultrafast Doppler in human neonates helps early detection of white matter injury
Flora Faure, Jérôme Baranger, Marianne Alison, Béatrice Boutillier, Alice Frérot, Chung Lim, Grégory Planchette, Mickael Prigent, Mickaël Tanter, Olivier Baud, Valérie Biran and Charlie Demené
Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism. 2024, 0(0); https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X241232197
Published: 10 February 2024
In this article the researchers show that using ultrafast Doppler imaging (UfD) it is possible to derive automated resistivity index (RI) measurements over the whole brain and the local vessel diameter, enabling for the first time the ability to relate the two quantities throughout the vascular tree. They present a quantitative assessment of cerebrovascular RI in generally overlooked small vessels and quantification of the RI versus vessel diameter in a large cohort of human neonates. The results demonstrate the potential of UfD and brain-wide resistivity quantification as new biomarkers, paving the way for UfD to be used for continuous monitoring of neonatal brain resistivity.
Hypothermia combined with extracellular vesicles from clonally expanded immortalized mesenchymal stromal cells improves neurodevelopmental impairment in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury
Nicole Labusek, Parnian Ghari, Yanis Mouloud, Christian Köster, Eva Diesterbeck, Martin Hadamitzky, Ursula Felderhoff-Müser, Ivo Bendix, Bernd Giebel and Josephine Herz
J Neuroinflammation 2023, 20, 280; https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-023-02961-0
Received: 8 September 2023 / Accepted: 16 November 2023 / Published: 27 November 2023
In this study the researchers hypothesised that intranasal administration of clonally expanded immortalised mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles can overcome limitations of hypothermia as a therapy for hypoxic–ischemic encephalopathy. Therapeutic hypothermia is used to treat neonatal brain injury following hypoxia–ischemia (decreased oxygen or blood flow to the brain) but has limitations due to its short therapeutic window of six hours and limited efficacy.
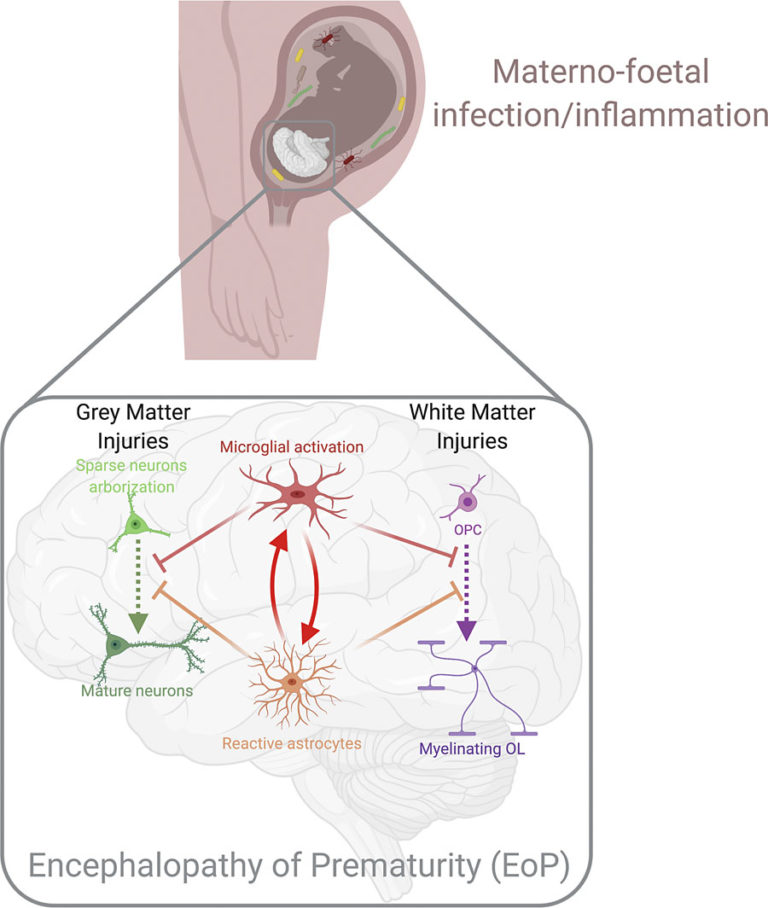
Key roles of glial cells in the encephalopathy of prematurity
Juliette Van Steenwinckel, Cindy Bokobza, Mireille Laforge, Isabelle K. Shearer, Veronique E. Miron, Rejane Rua, Samantha M. Matta, Elisa L. Hill-Yardin, Bobbi Fleiss and Pierre Gressens
Glia. 2023, 1–29; https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.24474
Received: 19 July 2023 / Revised: 17 September 2023 / Accepted: 19 September 2023 / Published: 1 November 2023
This review summarises the current state of knowledge for the roles of glia in infants with encephalopathy of prematurity (EoP) and its animal models, and a description of known glial-cell interactions in the context of EoP, such as the roles for border-associated macrophages. No longer just the ‘support cells’, we now clearly understand that during development glia are key for building a healthy brain. Glial dysfunction is a hallmark of EoP, notably, microgliosis, astrogliosis, and oligodendrocyte injury.
High sensitivity mapping of brain-wide functional networks in awake mice using simultaneous multi-slice fUS imaging
Adrien Bertolo, Jeremy Ferrier, Silvia Cazzanelli, Samuel Diebolt, Mickael Tanter, Sophie Pezet, Mathieu Pernot, Bruno-Félix Osmanski and Thomas Deffieux
Imaging Neuroscience 2023; https://doi.org/10.1162/imag_a_00030
Received: 12 July 2023 / Revised: 12 October 2023 / Accepted: 13 October 2023 / Published: 23 October 2023
In this study the researchers propose a new hybrid solution optimised and dedicated to brain-wide transcranial functional connectivity studies in mice, based on a newly developed multi-array transducer allowing simultaneous multi-slicing of the entire mouse cerebrum. They demonstrate that their approach provides a better imaging quality compared to other existing methods. They also show the ability to image the whole mouse brain non-invasively through the intact skin and skull during visual stimulation under light anaesthesia to validate this new approach.
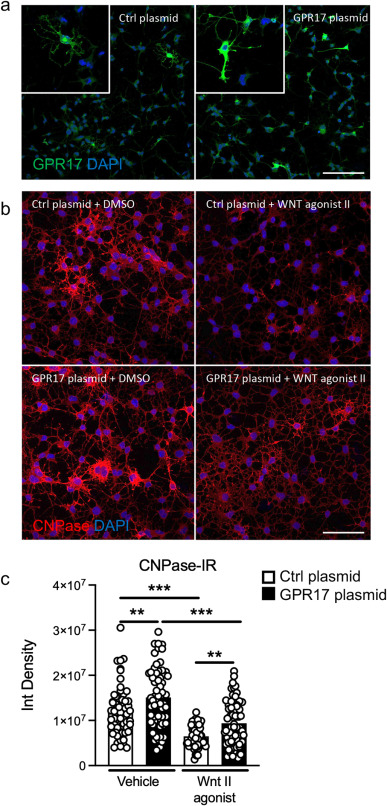
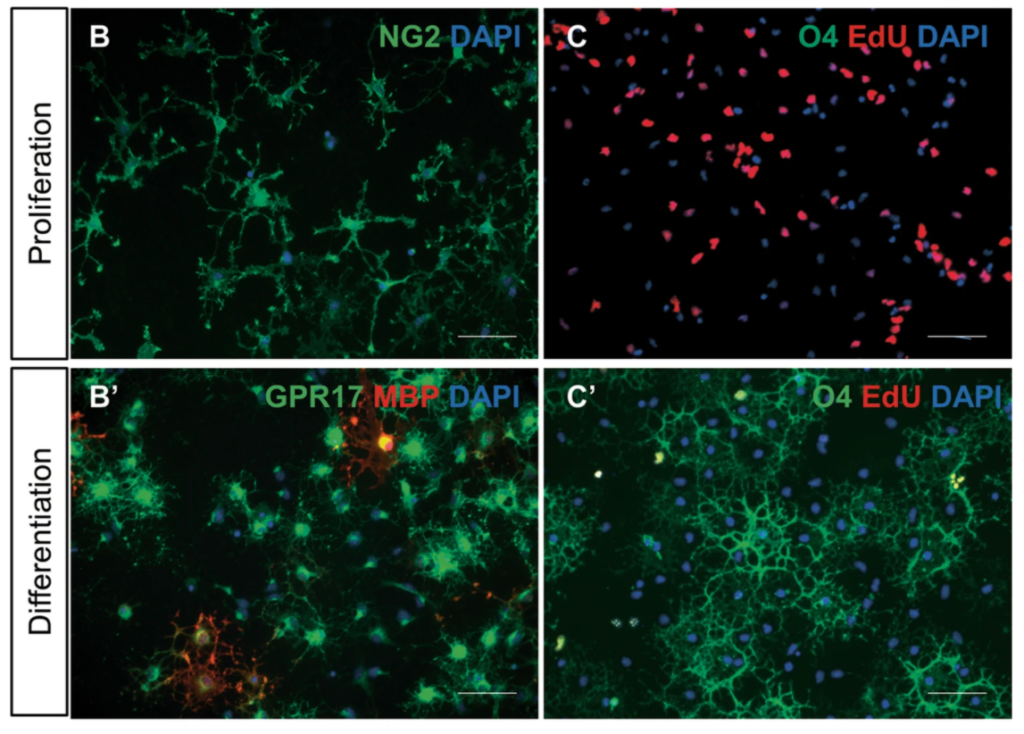
G protein-coupled receptor 17 is regulated by WNT pathway during oligodendrocyte precursor cell differentiation
Marta Boccazzi, Giulia Macchiarulo, Sophie Lebon, Justyna Janowska, Tifenn Le Charpentier, Valérie Faivre, Jennifer Hua, Davide Marangon, Davide Lecca, Marta Fumagalli, Shyamala Mani, Maria P. Abbracchio, Pierre Gressens, Anne-Laure Schang and Juliette Van Steenwinckel
Neurobiology of Disease 2023, Volume 187, 106315; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2023.106315
Received: 21 July 2023 / Revised: 13 September 202 / Accepted: 29 September 2023 / Available online: 30 September 2023
Using a combined pharmacological and biotechnological approach, the researchers examined regulatory mechanisms linking WNT signalling to GPR17 expression in oligodendrocytes.
Preterm Birth by Cesarean Section: The Gut-Brain Axis, a Key Regulator of Brain Development
Cécile Morin, Cindy Bokobza, Bobbi Fleiss, Elisa L. Hill-Yardin, Juliette Van Steenwinckel and Pierre Gressens
Dev Neurosci 2023; https://doi.org/10.1159/000534124
Received: 13 July 2022 / Accepted: 11 September 2023 / Published: 15 September 2023
In this review, the researchers explore links between preterm birth by caesarean sections (C-sections), gut microbiota alteration and neuroinflammation, highlighting C-sections (global rates of which are on the rise) as a risk factor for developmental disorders due to alterations in the microbiome. The mode of delivery or preterm birth are both factors which could lead to disturbance in the assembly and maturation of gut microbiota, with recent research highlighting how gut microbiota could affect brain development and behaviour.
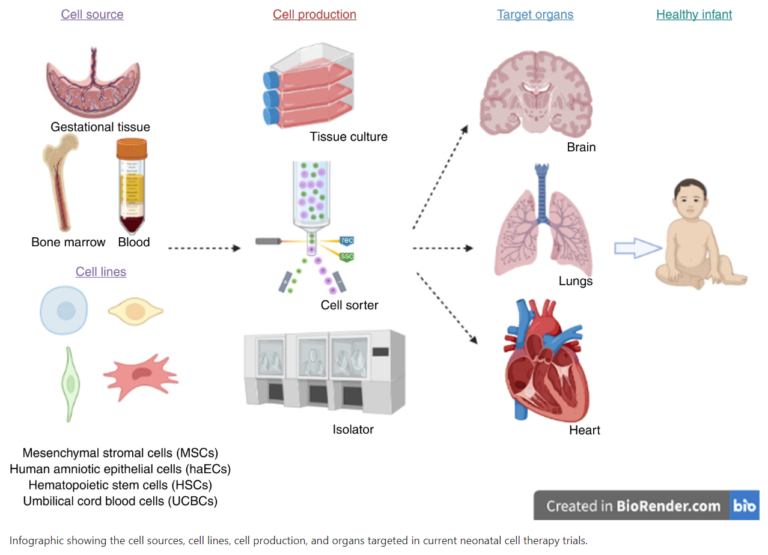
Advances in neonatal cell therapies: Proceedings of the First Neonatal Cell Therapies Symposium (2022)
Atul Malhotra, Bernard Thebaud, Madison C. B. Paton, Bobbi Fleiss, Paris Papagianis, Elizabeth Baker, Laura Bennet, Tamara Yawno, Ngaire Elwood, Belinda Campbell, Kirat Chand, Lindsay Zhou, Tayla Penny, Timothy Nguyen, Salvatore Pepe, Alistair J. Gunn and Courtney A. McDonald
Pediatr Res 2023; https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-023-02707-x
Received: 16 February 2023 / Revised: 8 May 2023 / Accepted: 8 June 2023 / Published: 28 June 2023
With advances in neonatal medicine, the survival of preterm and sick term newborn infants has improved substantially. Rates of preterm complications like chronic lung disease, brain injury and pulmonary hypertension remain high, as do the risks of long-term neurodevelopmental, pulmonary, cardiac and metabolic complications. This article summarises highlights from the 2022 Neonatal Cell Therapies Symposium where researchers presented the latest on cell therapies in the neonate and their potential to repair, protect, and in some cases regenerate vital body tissues.
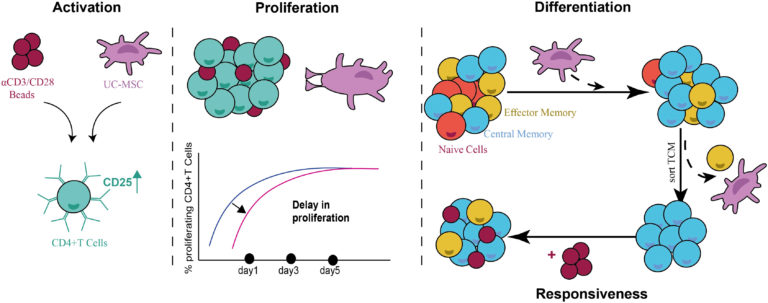
Umbilical cord-mesenchymal stem cells induce a memory phenotype in CD4+ T cells
Ezgi Sengun, Tim G. A. M. Wolfs, Valéry L. E. van Bruggen, Bram van Cranenbroek, Elles R. Simonetti, Daan Ophelders, Marien I. de Jonge, Irma Joosten and Renate G. van der Molen
Front. Immunol. 2023, 14:1128359; https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1128359
Received: 20 December 2022 / Accepted: 1 June 2023 / Published: 20 June 2023
This study assessed the immunomodulatory effect of umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells (UC-MSCs) on T cell phenotype and function, with a focus on activation, proliferation and maturation of CD4+ T cells with the aim of better understanding the UC-MSC mode of action. The data show that UC-MSCs clearly affect T cell activation, proliferation and maturation, depending on co-culture conditions for which both cell-cell contact and paracrine factors are needed.
Targeting the brain 5-HT7 receptor to prevent hypomyelination in a rodent model of perinatal white matter injuries
Cindy Bokobza, Alice Jacquens, David Guenoun, Blandine Bianco, Anne Galland, Maxime Pispisa, Alexandra Cruz, Manuela Zinni, Valérie Faivre, Anne Roumier, Sophie Lebon, Tania Vitalis, Zsolt Csaba, Tifenn Le Charpentier, Leslie Schwendimann, Pierrette Young-Ten, Vincent Degos, Patricia Monteiro, Pascal Dournaud, Pierre Gressens and Juliette Van Steenwinckel
J Neural Transm. 2022; https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-022-02556-8
Received: 8 July 2022 / Accepted: 19 October 2022 / Published: 6 November 2022
In this article the research team highlights the concept of the HTR7 (5-HT receptor subtype 7) regulating brain inflammation in a context of white matter injury induced by perinatal exposure that models neurodevelopmental disorders associated with prematurity, including memory deficits, anxiety-like-behaviour, and deficits in social interactions. These data open new perspectives for therapy to protect the developing brain from the adverse effects of early immune activation.
The multiple faces of extracellular vesicles released by microglia: Where are we 10 years after?
Martina Gabrielli, Stefano Raffaele, Marta Fumagalli and Claudia Verderio
Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16:984690; https;//10.3389/fncel.2022.984690
Received: 2 July 2022 / Accepted: 23 August 2022 / Published: 13 September 2022
The review summarises the current knowledge on extracellular vesicles released by microglia, highlighting
their heterogeneous properties and multifaceted effects.
Magnetic Isolation of Microglial Cells from Neonate Mouse for Primary Cell Cultures
Cindy Bokobza, Alice Jacquens, Manuela Zinni, Valérie Faivre, Jennifer Hua, David Guenoun, Caroline
Userovici, Shyamala Mani, Vincent Degos, Pierre Gressens and Juliette Van Steenwinckel
J. Vis. Exp. 2022, (185), e62964; https://doi.org/10.3791/62964
Published: 25 July 2022
The paper describes a protocol which aims to get as close as possible to the physiological environment of microglia. Besides requiring no serum, the protocol exposes microglia as early as 48 hours after culture to prevent them from losing their physiological faculties.
Download PDF of Magnetic Isolation of Microglial Cells from Neonate Mouse for Primary Cell Cultures
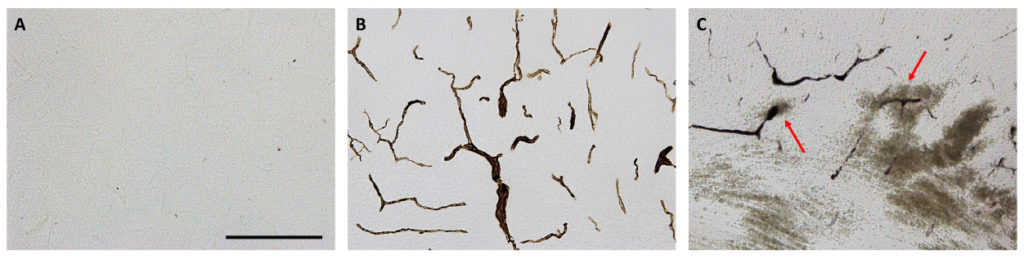
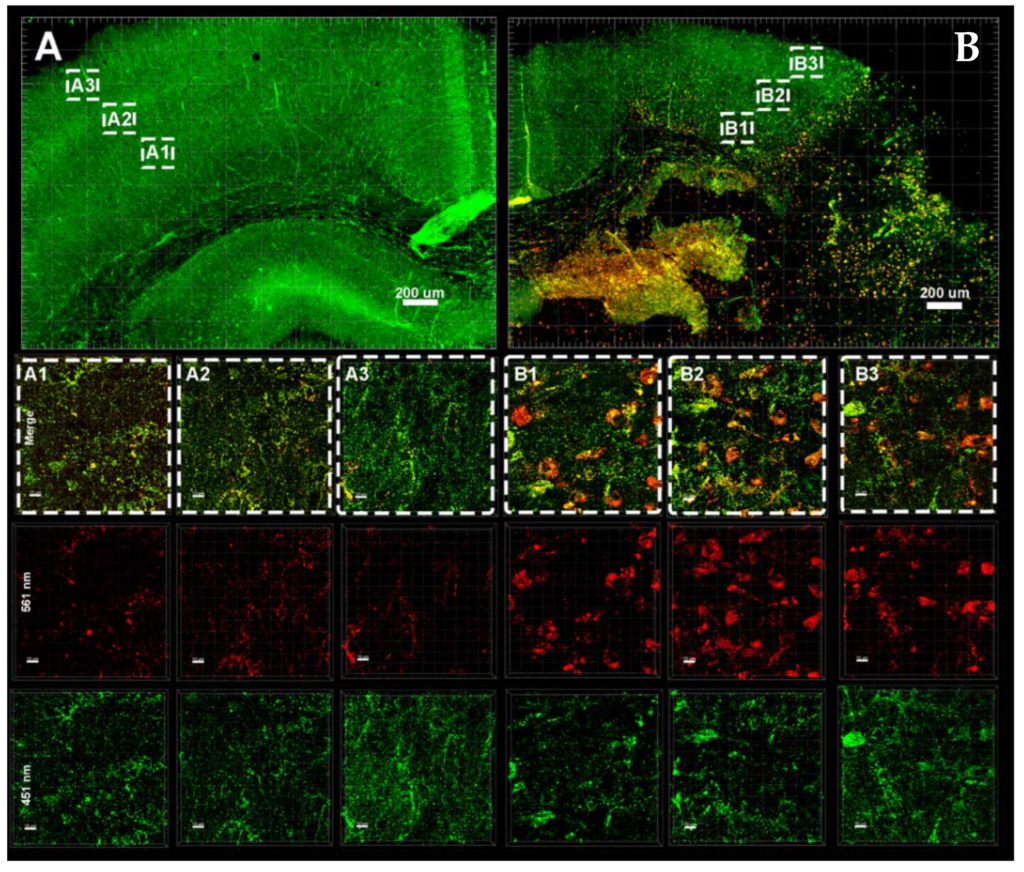
A unique cerebellar pattern of microglia activation in a mouse model of encephalopathy of prematurity
Luisa Klein, Juliette Van Steenwinckel, Bobbi Fleiss, Till Scheuer, Christoph Bührer, Valerie Faivre, Sophie Lemoine, Corinne Blugeon, Leslie Schwendimann, Zsolt Csaba, Cindy Bokobza, Dulcie A. Vousden, Jason P. Lerch, Anthony C. Vernon, Pierre Gressens and Thomas Schmitz
Glia. 2022, 70:1699–1719; https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.24190
Received: 16 October 2021 / Revised: 26 April 2022 / Accepted: 29 April 2022 / Published: 27 April 2022
This study used a mouse model of inflammation-induced encephalopathy of prematurity driven by systemic administration of pro-inflammatory IL-1β to look to uncover causes of cerebellar damage, which is associated with impaired motor performance, lower IQ and poor language skills at school ages.
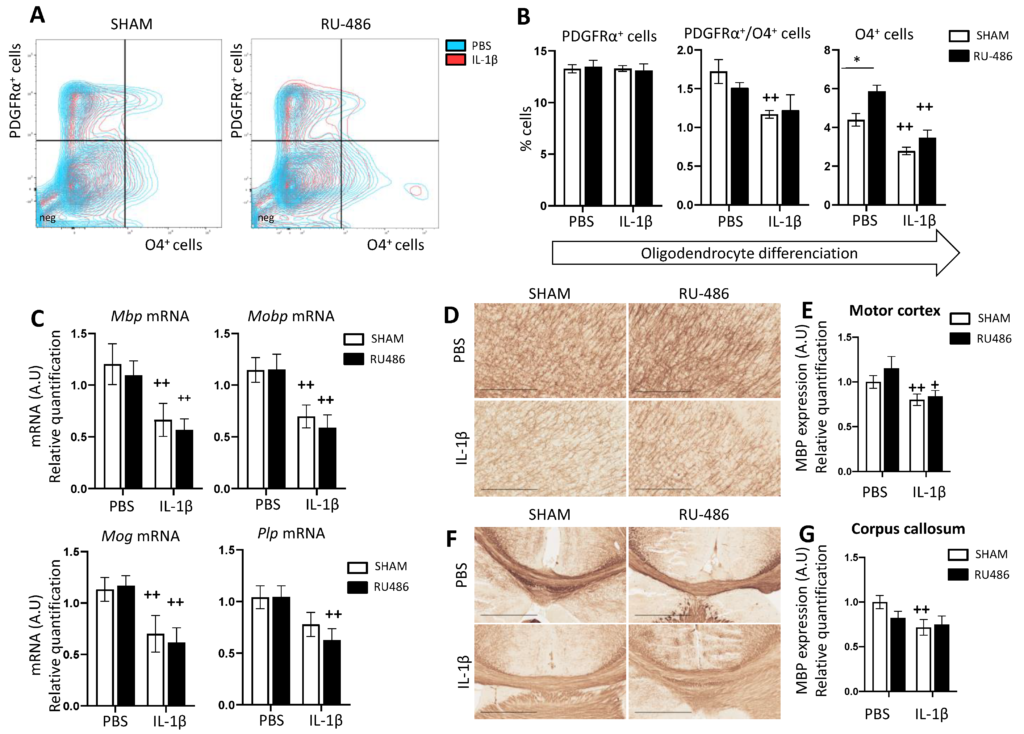
The Impact of Mouse Preterm Birth Induction by RU-486 on Microglial Activation and Subsequent Hypomyelination
Cécile Morin, David Guenoun, Irvin Sautet, Valérie Faivre, Zsolt Csaba, Leslie Schwendimann, Pierrette Young-Ten, Juliette Van Steenwinckel, Pierre Gressens and Cindy Bokobza
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23(9), 4867; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094867
Received: 7 March 2022 / Revised: 21 April 2022 / Accepted: 21 April 2022 / Published: 27 April 2022
This study aimed to elaborate and characterise a new model of induced-PTB and PWMIs by the gestational injection of RU-486 and the perinatal injection of pups with IL-1beta. A RU-486 single subcutaneous (s.c.) injection at embryonic day (E)18.5 induced PTB at E19.5 in pregnant OF1 mice.
Induction of Mitochondrial Fragmentation and Mitophagy after Neonatal Hypoxia–Ischemia
Syam Nair, Anna-Lena Leverin, Eridan Rocha-Ferreira, Kristina S. Sobotka, Claire Thornton, Carina Mallard and Henrik Hagberg
Cells 2022, 11, 1193; https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11071193
Received: 20 December 2021 / Accepted: 30 March 2022 / Published: 1 April 2022
This study investigated mitochondrial dynamics (fission, fusion, and mitochondrial autophagy (mitophagy) after HI in vivo in mice and oxygen/glucose deprivation (OGD) in vitro in primary neurons. It also analysed genes/proteins related to mitophagy after HI including PINK1/Parkin, BNIP3/NIX and FUNDC1. The data suggest
that OGD triggers mitochondrial fragmentation and an early increase in mitophagy.
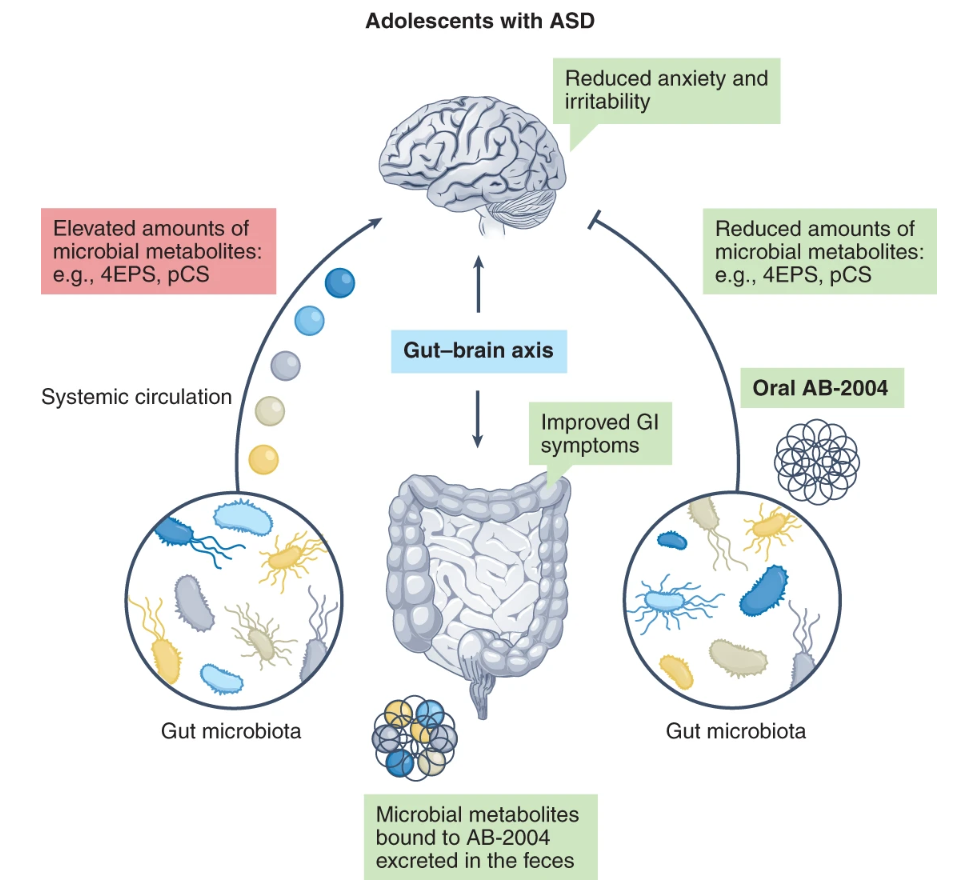
Targeting microbial metabolites to treat autism
Rochellys Diaz Heijtz, Pierre Gressens and Jonathan R. Swann
Nat Med 2022, 28, 448–450; https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-022-01711-8
Published: 14 February 2022
This article discusses data presented by Campbell et al. and Needham et al. in the study of the microbiota–gut–brain axis as researchers continue to find treatments to improve core symptoms of autism spectrum disorder, such as irritability and anxiety.
Download PDF of Targeting microbial metabolites to treat autism
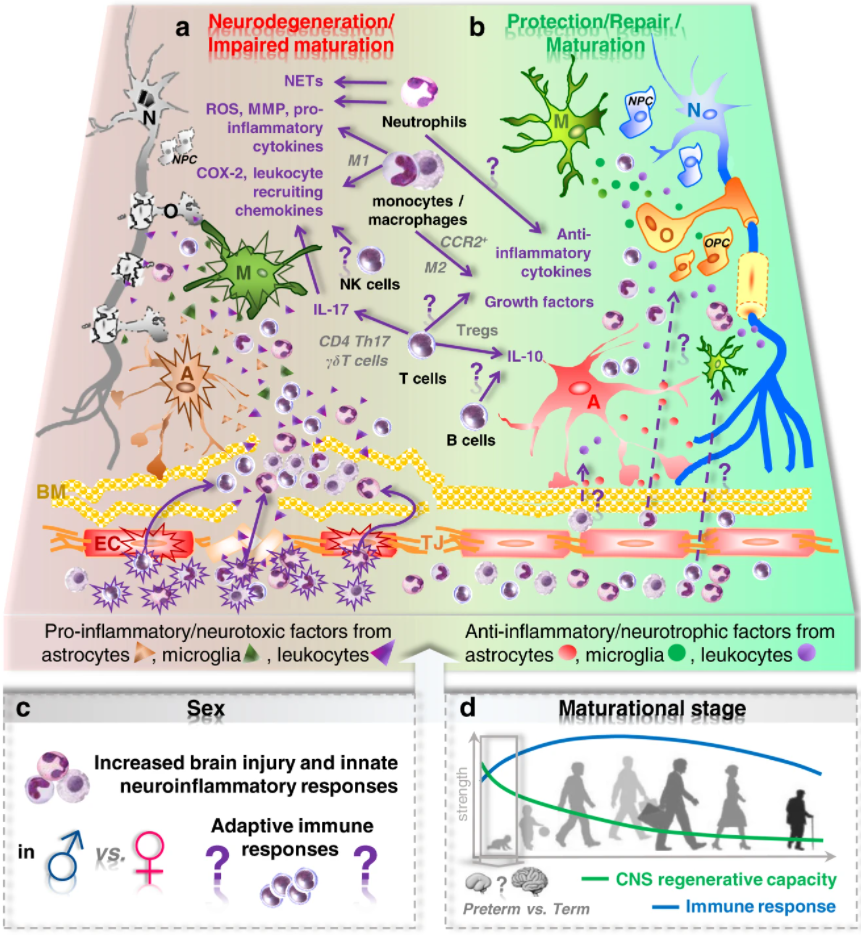
Peripheral immune cells and perinatal brain injury: a double-edged sword?
Josephine Herz, Ivo Bendix and Ursula Felderhoff-Müser
Pediatr Res 2022, 91, 392–403; https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-021-01818-7
Received: 15 June 2021 / Revised: 24 August 2021 / Accepted: 14 September 2021 / Published: 8 November 2021
This review focuses on the role of peripheral immune cells and discusses processes involved in neuroinflammation under two frequent perinatal conditions, systemic infection/inflammation associated with encephalopathy of prematurity (EoP) and hypoxia/ischaemia in the context of neonatal encephalopathy and stroke at term. Different immune cell subsets in perinatal brain injury including their infiltration routes were reviewed and critical aspects such as sex differences and maturational stage discussed. Interactions with existing regenerative therapies such as stem cells and also potentials to develop novel immunomodulatory targets were considered.
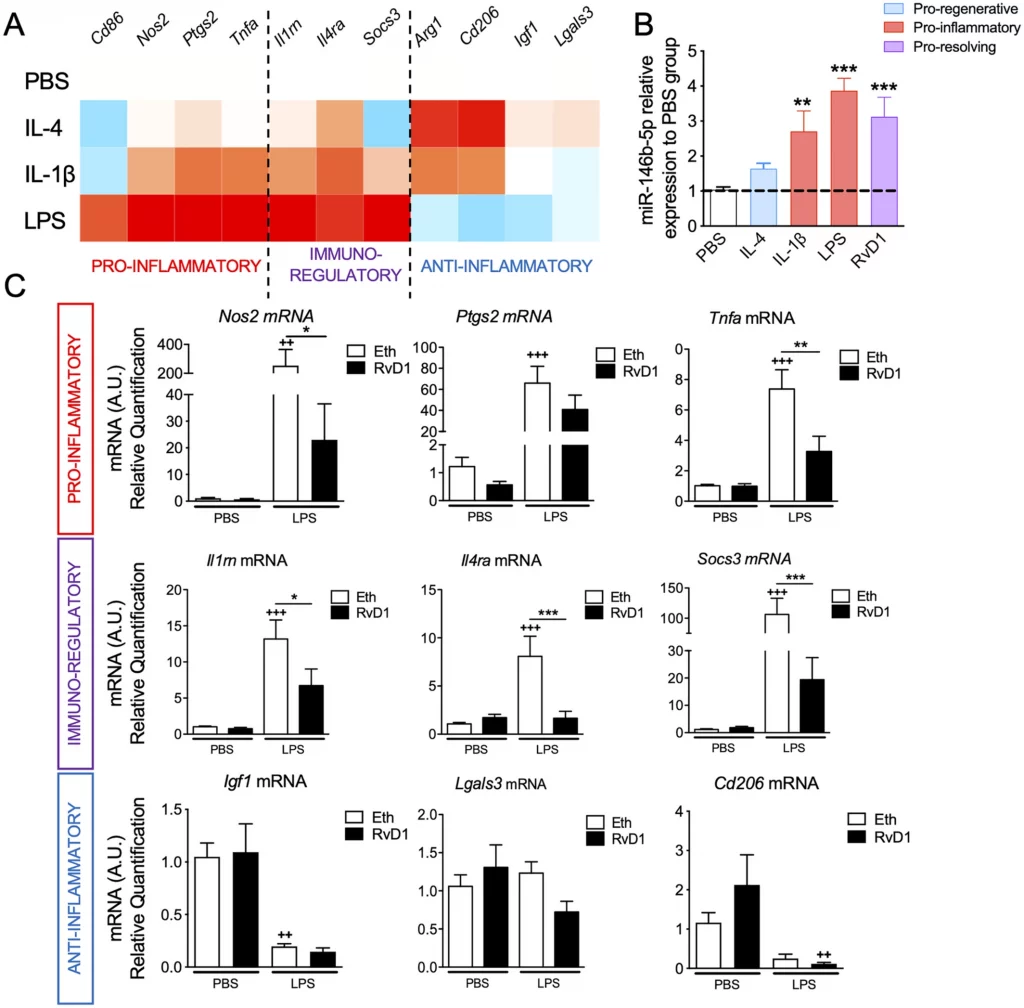
miR-146b Protects the Perinatal Brain against Microglia-Induced Hypomyelination
Cindy Bokobza, Pooja Joshi, Anne-Laure Schang, Zsolt Csaba, Valérie Faivre, Amélie Montané, Anne Galland, Anouk Benmamar-Badel, Emmanuelle Bosher, Sophie Lebon, Leslie Schwendimann, Shyamala Mani, Pascal Dournaud, Valerie Besson, Bobbi Fleiss, Pierre Gressens and Juliette Van Steenwinckel
Ann Neurol. 2021; https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.26263
Received: 7 May 2020 / Accepted: 3 November 2021 / Available online: 5 November 2021
In the preterm newborn, perinatal inflammation mediated by microglia contributes significantly to neurodevelopmental injuries including white matter injury (WMI). This study demonstrates that miR-146b acts as a negative feedback mechanism against inflammatory activation specifically in microglia in a model of WMI, demonstrating that miR mediated therapies may have a future as efficient strategies to protect the developing brain against WMI.
The immune-inflammatory response of oligodendrocytes in a murine model of preterm white matter injury: the role of TLR3 activation
Marta Boccazzi, Juliette Van Steenwinckel, Anne-Laure Schang, Valérie Faivre, Tifenn Le Charpentier, Cindy Bokobza, Zsolt Csaba, Claudia Verderio, Marta Fumagalli, Shyamala Mani and Pierre Gressens
Cell Death Dis 2021, 12, 166; https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-021-03446-9
Received: 2 June 2020 / Revised: 13 December 2020 / Accepted: 3 January 2021 / Available online: 8 February 2021
This study focused on toll-like receptor-3, a protein activated by double-strand RNA, which promotes neuroinflammation. The aim was to better understand its expression and role in oligodendrocytes (one of the last types of cell to form in the brain). The in vivo mouse model mimicked white matter injury occurring in preterm babies.
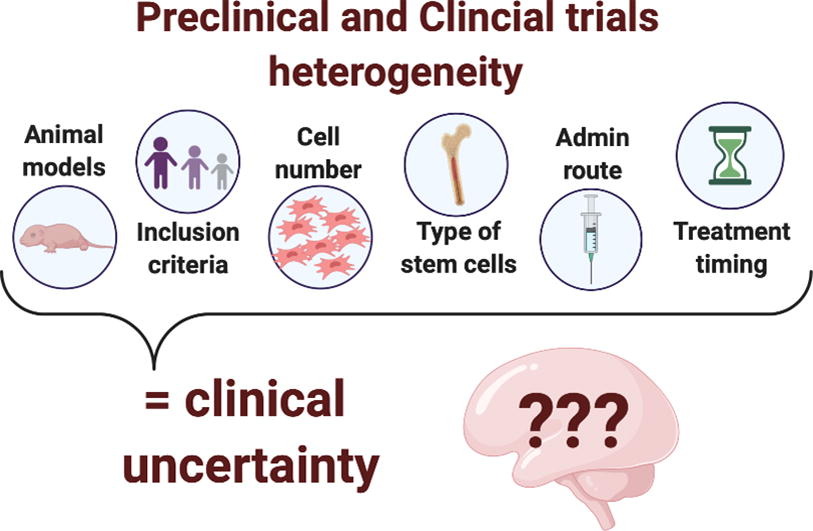
Therapeutic potential of stem cells for preterm infant brain damage: can we move from the heterogeneity of preclinical and clinical studies to established therapeutics?
Sofia Passera, Marta Boccazzi, Cindy Bokobza, Valerie Faivre, Fabio Mosca, Juliette Van Steenwinckel, Monica Fumagalli, Pierre Gressens and Bobbi Fleiss
Biochemical Pharmacology 2021, 114461; https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11010099
Received: 10 December 2020 / Revised: 27 January 2021 / Accepted: 2 February 2021 / Available online: 8 February 2021
In this review, the researchers summarise and discuss preclinical and clinical investigations which have studied stem cells as an effective neuroprotectant for perinatal brain injury.
Microglia-Mediated Neurodegeneration in Perinatal Brain Injuries
Bobbi Fleiss, Juliette Van Steenwinckel, Cindy Bokobza, Isabelle K. Shearer, Emily Ross-Munro and Pierre Gressens
Biomolecules 2021, 11(1), 99; https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11010099
Received: 29 November 2020 / Revised: 8 January 2021 / Accepted: 11 January 2021 / Published: 13 January 2021
This review looks at strategies developed experimentally to modulate microglia and reduce brain injury in babies. It focusses on four causes of perinatal brain injury which occur frequently in both westernised and emerging countries, including EoP and neonatal stroke, and reviews pharmacological approaches as well as novel nanoparticle mediated therapies.
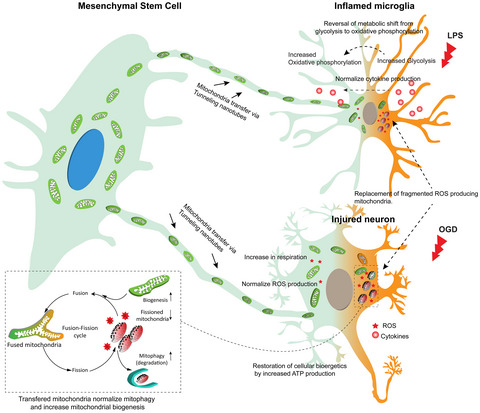
Neuroprotection offered by mesenchymal stem cells in perinatal brain injury: Role of mitochondria, inflammation, and reactive oxygen species
Syam Nair, Eridan Rocha-Ferreira, Bobbi Fleiss, Cora H Nijboer, Pierre Gressens, Carina Mallard and Henrik Hagberg
Journal of Neurochemistry 2021, 2021;158:59–73; https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.15267
Received: 15 July 2020 / Revised: 3 December 2020 / Accepted: 3 December 2020 / Published: 12 December 2020
This review summarises the present state, the underlying causes, challenges and possibilities for effective clinical translation of mesenchymal stem cell therapy.
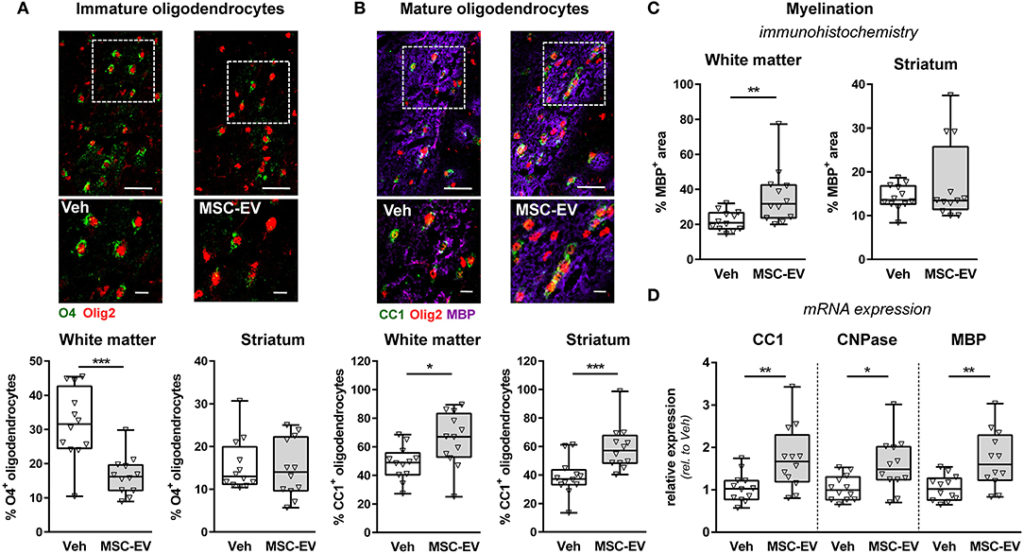
Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Reduce Neuroinflammation, Promote Neural Cell Proliferation and Improve Oligodendrocyte Maturation in Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury
Nicole Kaminski, Christian Köster, Yanis Mouloud, Verena Börger, Ursula Felderhoff-Müser, Ivo Bendix, Bernd Giebel and Josephine Herz
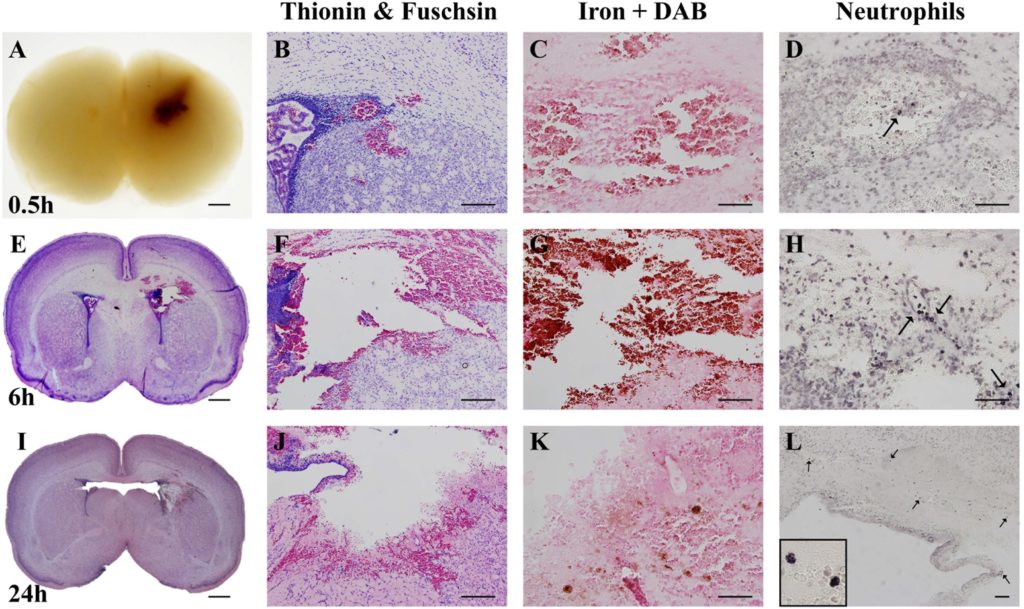
A Model of Germinal Matrix Hemorrhage in Preterm Rat Pups
Masako Jinnai, Gabriella Koning, Gagandeep Singh-Mallah, Andrea Jonsdotter, Anna-Lena Leverin, Pernilla Svedin, Syam Nair, Satoru Takeda, Xiaoyang Wang, Carina Mallard, Carl Joakim Ek, Eridan Rocha-Ferreira and Henrik Hagberg
Preterm Brain Injury, Antenatal Triggers, and Therapeutics: Timing Is Key
Daan R.M.G. Ophelders, Ruth Gussenhoven, Luise Klein, Reint K. Jellema, Rob J.J. Westerlaken, Matthias C. Hütten, Jeroen Vermeulen, Guido Wassink, Alistair J. Gunn and Tim G.A.M. Wolfs
Cortical Gray Matter Injury in Encephalopathy of Prematurity: Link to Neurodevelopmental Disorders
Bobbi Fleiss, Pierre Gressens and Helen B. Stolp
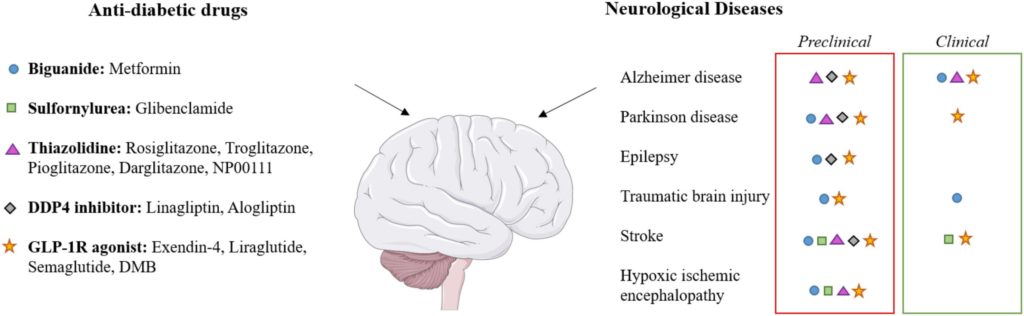
Neuroprotective Effects of Diabetes Drugs for the Treatment of Neonatal Hypoxia-Ischemia Encephalopathy
Laura Poupon-Bejuit, Eridan Rocha-Ferreira, Claire Thornton, Henrik Hagberg and Ahad A. Rahim
Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020 Sec. Cellular Neuropathology Volume 14: https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2020.00112
Received: 14 February 2020 / Accepted: 8 April 2020 / Published: 6 May 2020
In this review, the researchers describe the experimental and animal models of hypoxia-ischemia encephalopathy (HIE) that are used in preclinical studies to assess the therapeutic efficacy of candidate drugs. They then highlight the studies that support the potential of commonly used diabetes medicines to improve neurological damage from HIE.