Our research explained
About the brain
PREMSTEM research and the brain
Many of PREMSTEM’s researchers are experts in disorders related to the brain, such as cerebral palsy, and together bring years of experience studying different types of brain injury to the project. As a team, we’re trying to find a new therapy to reduce the effects of brain damage sometimes suffered by preterm babies.
On this page we share our interest in the brain – one of the body’s largest and most complex organs!
Humans only use 10% of their brains
False
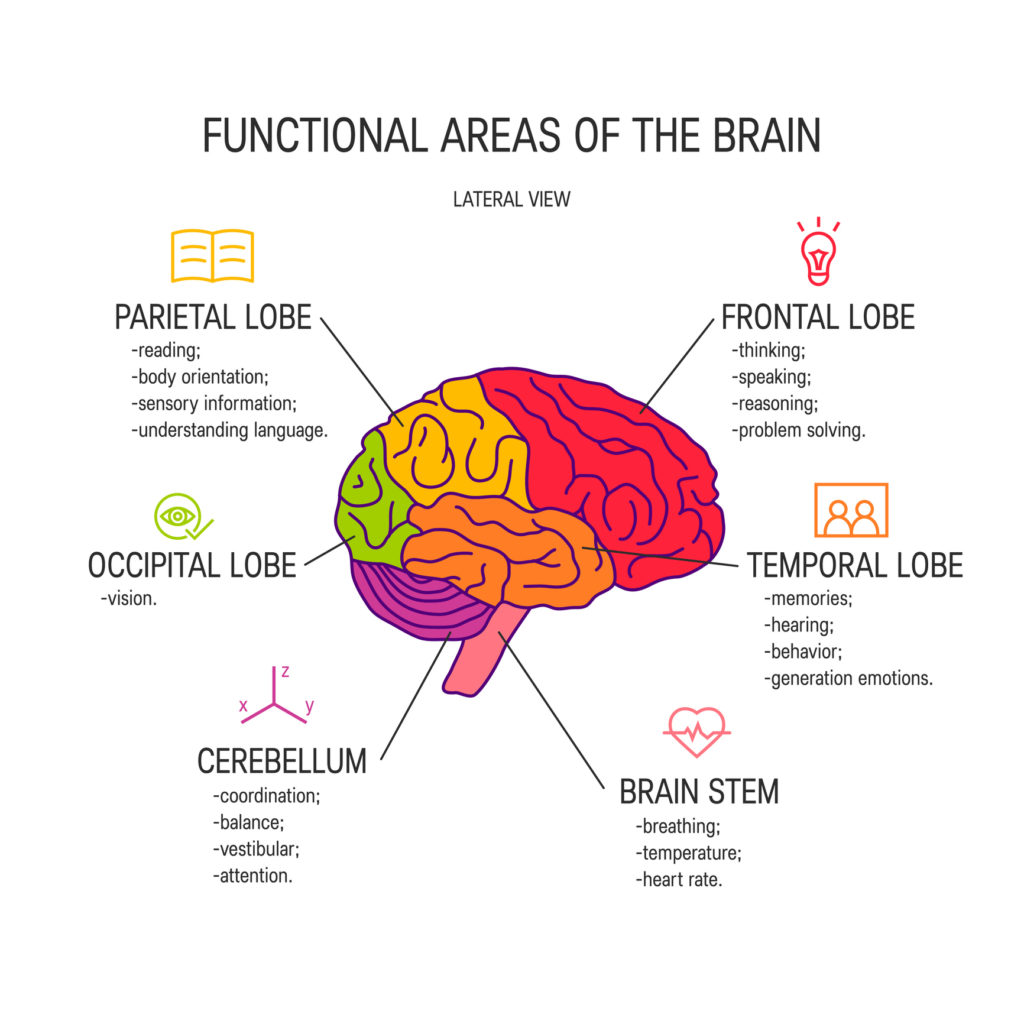
What is the structure of the brain?
The brain consists of different parts with different functions. They work together to allow us to perform different types of task, from standing up to breathing – tasks the average person does without even thinking.
- Cortex: The outermost layer of brain cells, the cortex is where thinking and voluntary movements originate.
- Brain stem: Between the spinal cord and the rest of the brain, the brain stem controls basic functions like breathing and sleep.
- Basal ganglia: A cluster of structures in the centre of the brain that coordinates messages between other areas of the brain.
- Cerebellum: At the base and back of the brain, the cerebellum is responsible for coordination and balance.
The brain’s four lobes are also involved in different types of everyday task and bodily function.
- Frontal lobes: Problem solving and judgement, motor function.
- Parietal lobes: Sensation, handwriting, body position.
- Temporal lobes: Memory, hearing.
- Occipital lobes: The location of the brain’s visual processing system.
Source: WebMD
Why is the brain vulnerable?
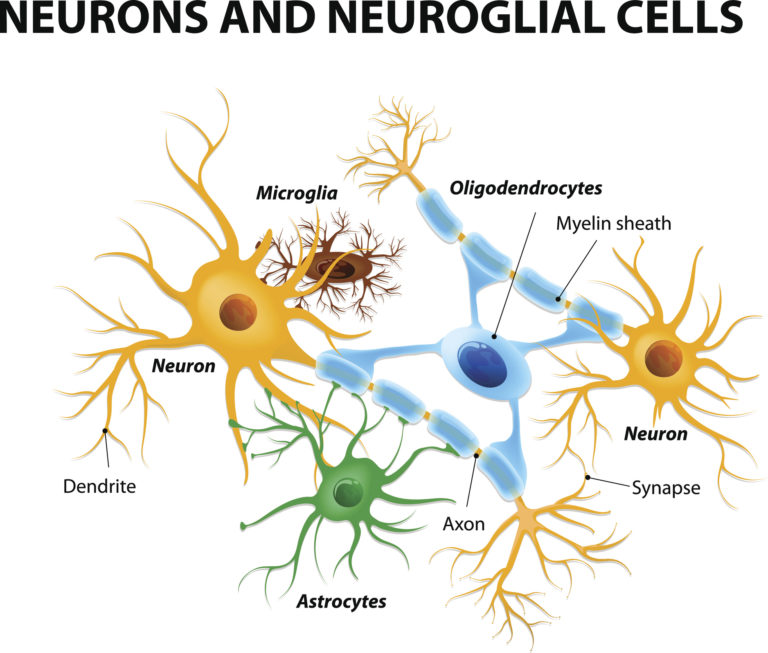
We all know that the brain is an important organ in our body. It’s also a very delicate and vulnerable one! To find out why, we’ve profiled different types of cell in the brain to find out what they do – and why a preterm birth can be disruptive to their development.
Brain cells
0:47
0:59
0:53
0:41
0:29
0:41
0:53
1:11
0:47
Bergmann glia are a type of astrocyte found alongside the Purkinje cells in the cerebellum. Bergman glia are numerous, outnumbering Purkinje cells 8 to 1! Bergmann glia play a role in the migration of granule cells up to the granule layer early in the development of the cerebellum. Like other astrocytes, Bergman glia play a supportive role to neurons and help to regulate the brain’s oxygen supply. They help to optimise the information processing and carry out housekeeping activities. They are also thought to be important for neuroprotection, playing a part in controlling calcium levels in the brain. Calcium imbalance has been linked to neurodegeneration and diseases like Alzheimer’s. Studies of brain injury related to preterm birth have shown that Bergman glia are also vulnerable to injury – with decreased number and altered shape and size.
Did you know?
A look inside the brain - images from the PREMSTEM labs
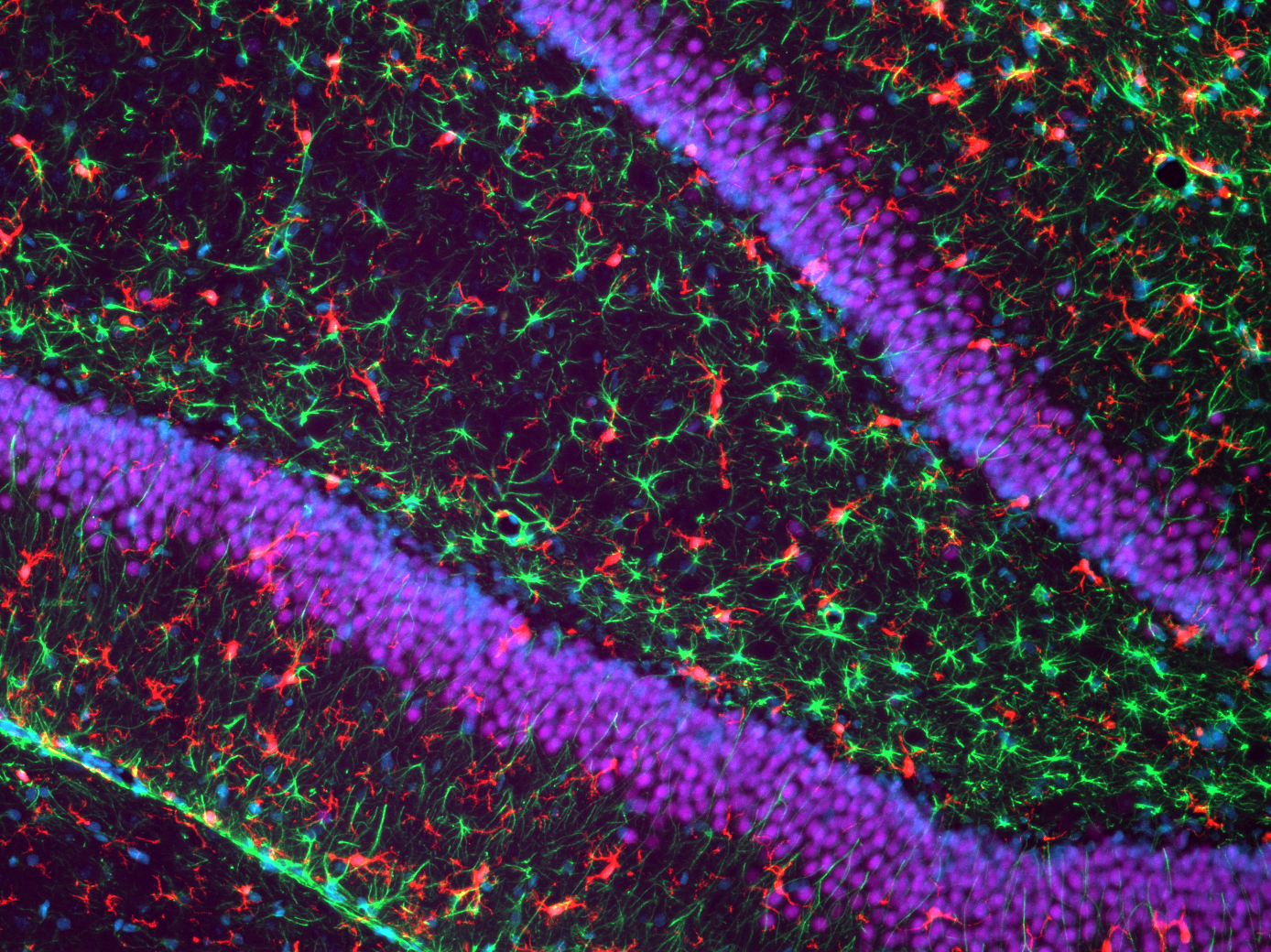
Magnification of the rat brain at the level of the hippocampus
Microglia in red, astrocytes in green, and neurons in purple with blue used as a counterstain.
Credit: Chantal Kosmeijer, UMC Utrecht
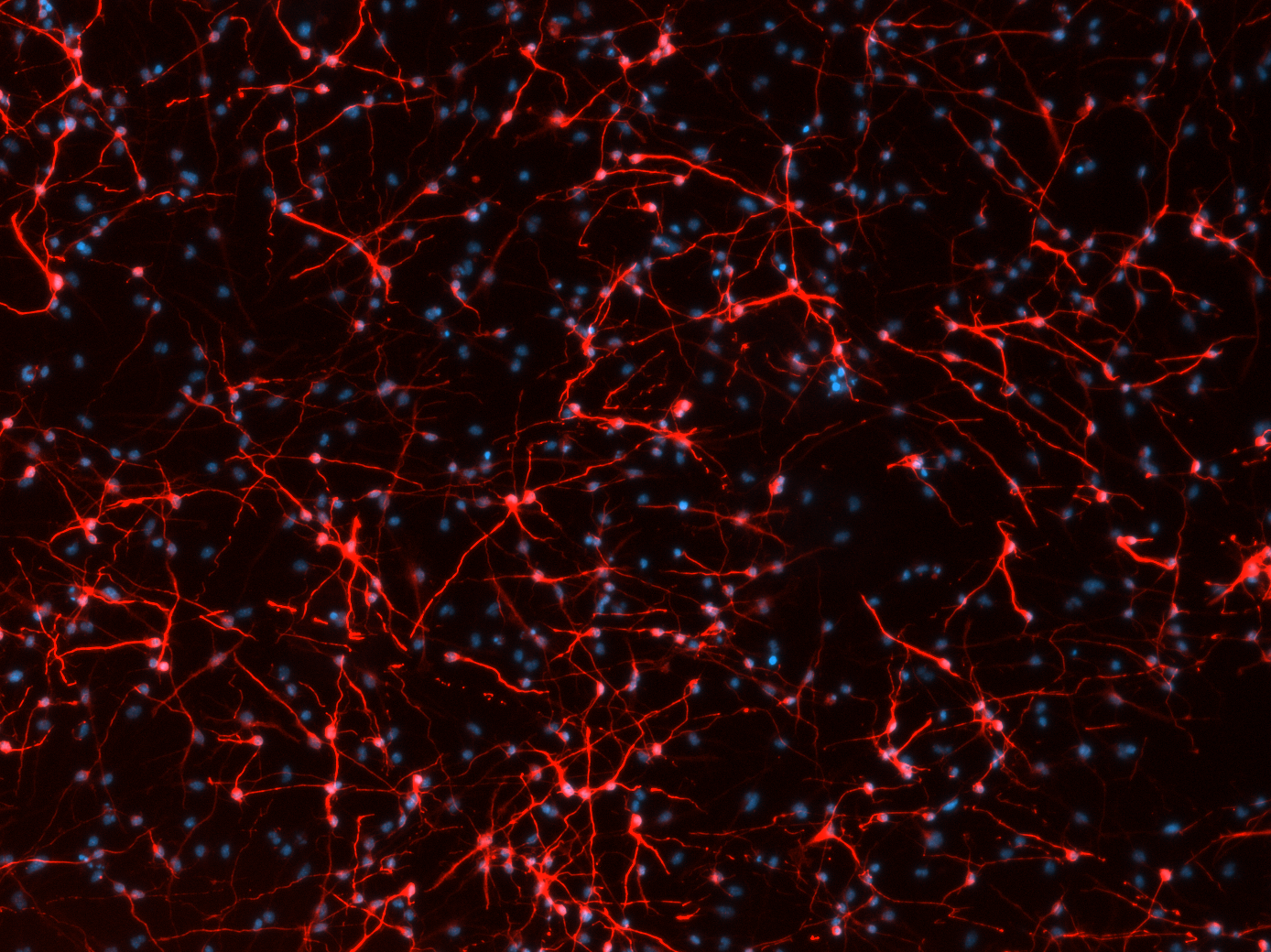
Neural stem cells differentiated in vitro towards neurons
Neural stem cells differentiated in vitro towards neurons which form networks in a dish, with blue used as a counterstain.
Credit: Sara De Palma, UMC Utrecht

Mouse brain with hypoxic-ischemic brain injury
A montage created using MRI showing hypoxic-ischemic brain injury.
Credit: Sara De Palma and group of Rick Dijkhuizen (Annette van der Toorn and Geralda van Tilborg), UMC Utrecht
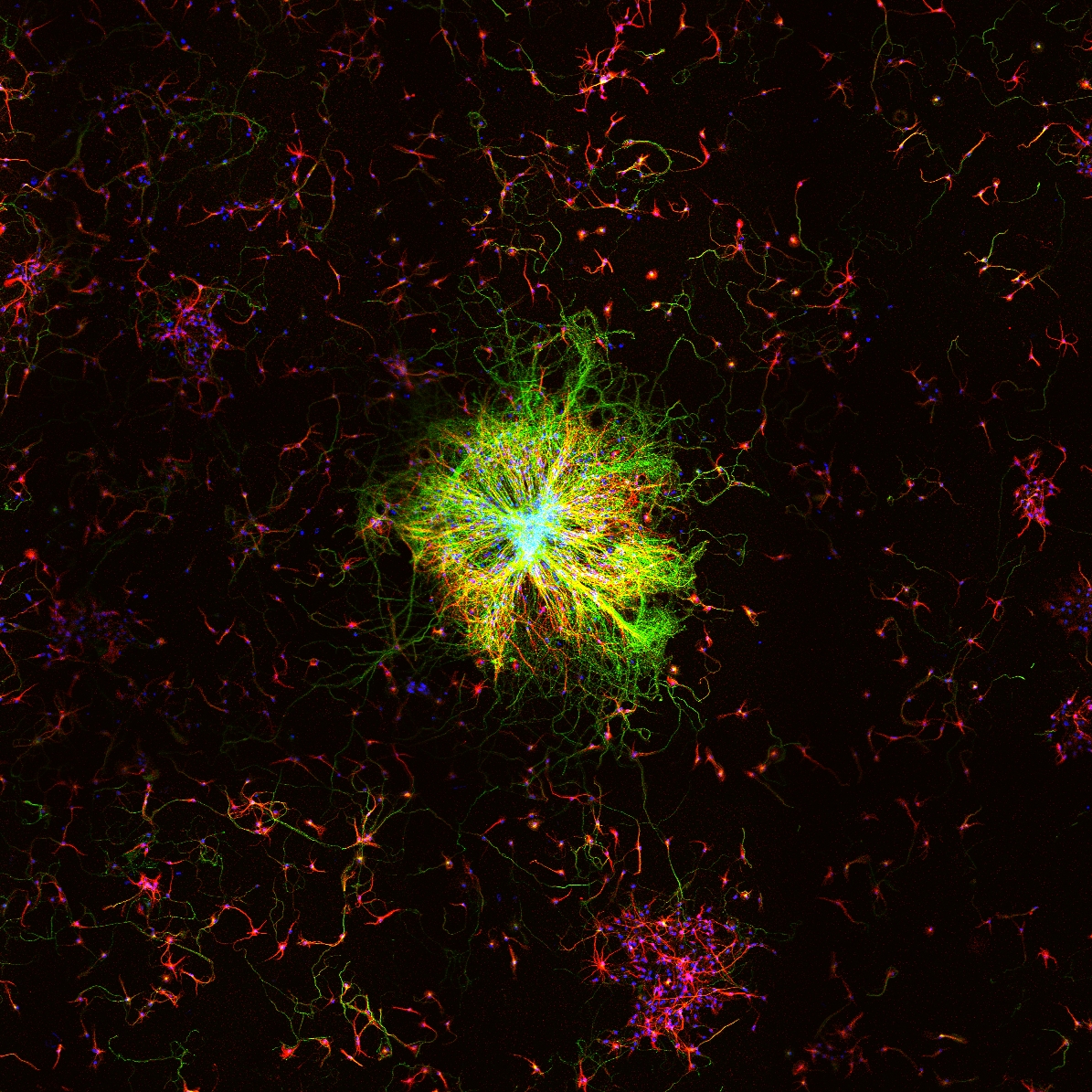
Hippocampal neurons after hyperoxia
Hippocampal neurons after hyperoxia, a state where there is too much oxygen, cultured together with human mesenchymal stem cells (h-MSCs).
Credit: Meray Sendar, Universitätsmedizin Essen
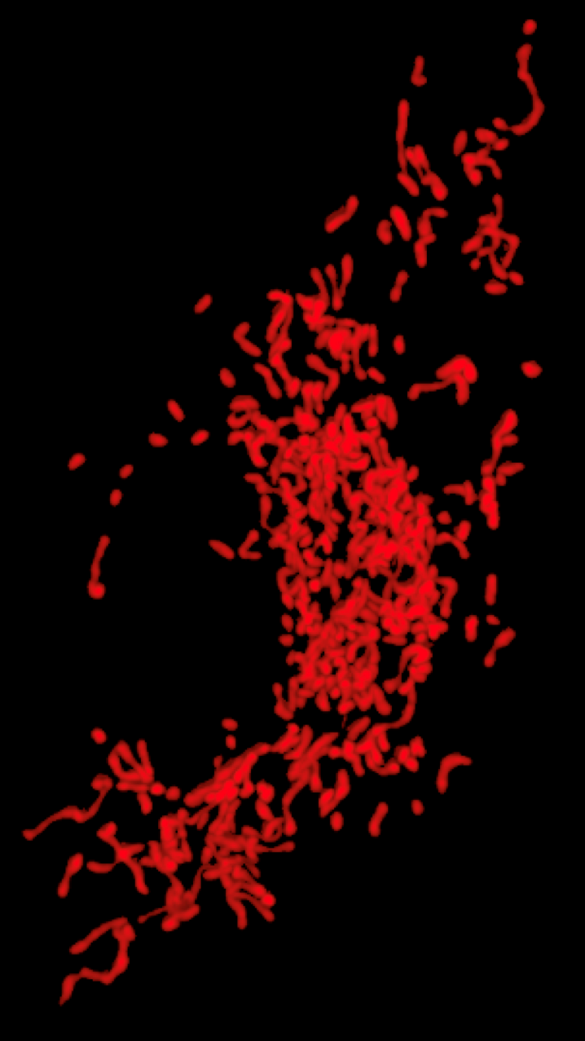

Mitochondria inside a single microglia cell
Credit: Syam Nair, University of Gothenburg
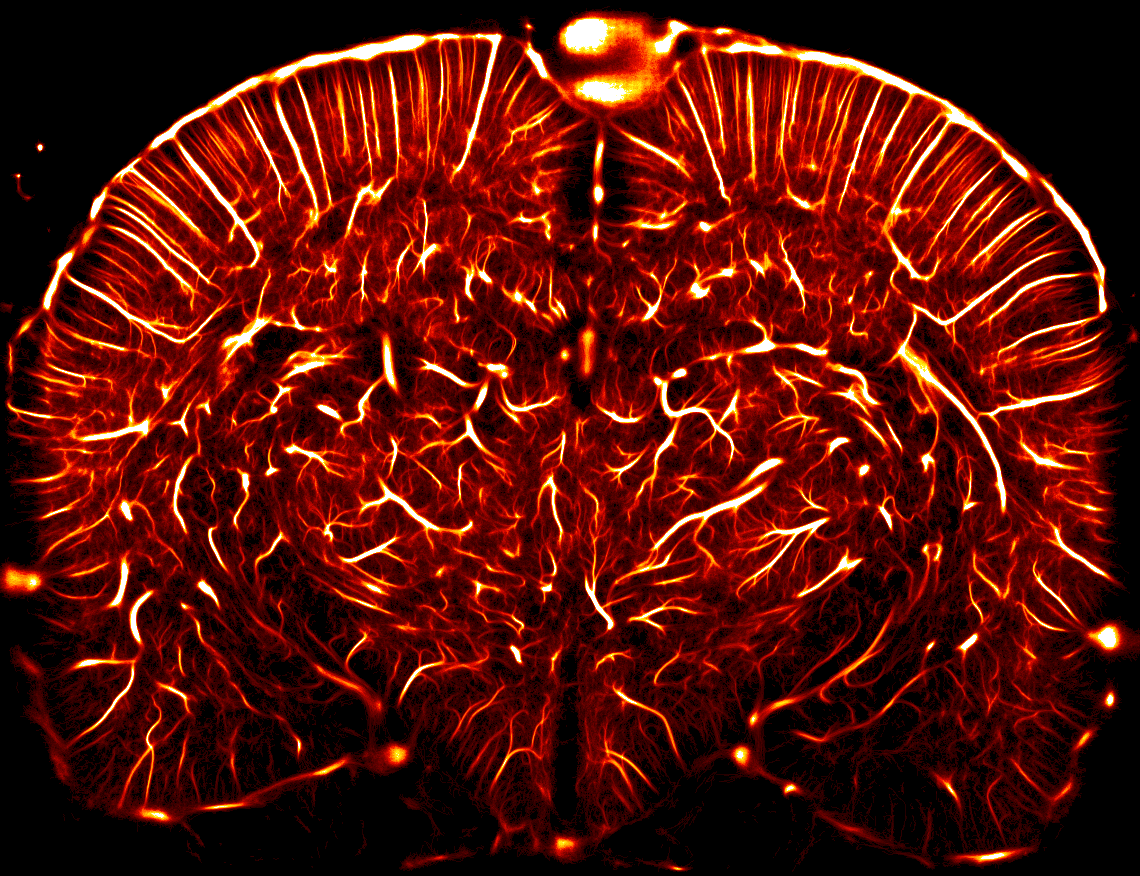
Vascular density of a complete coronal section of the living rat brain
Credit: Iconeus
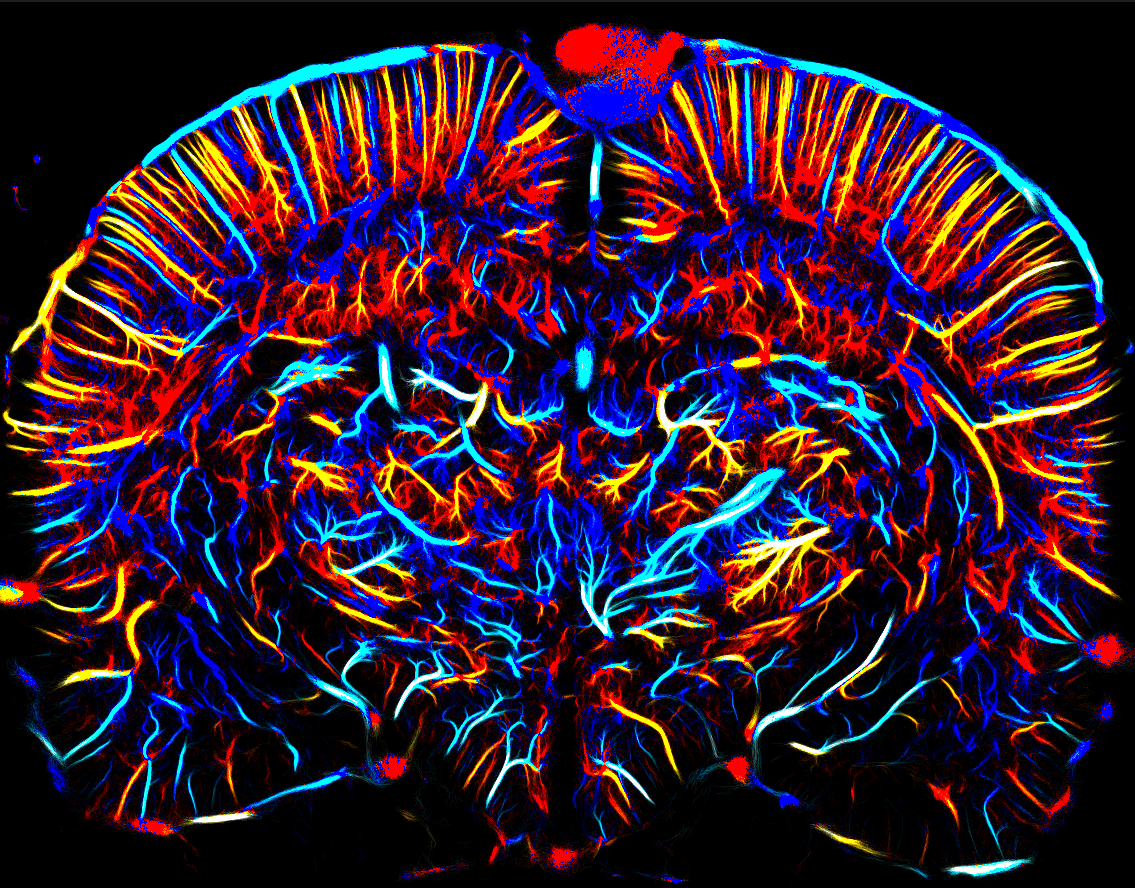
Axial velocities of gas microbubbles
Measured in the mm/s range and their direction (blue is upward flow, red is downward flow).
Credit: Iconeus
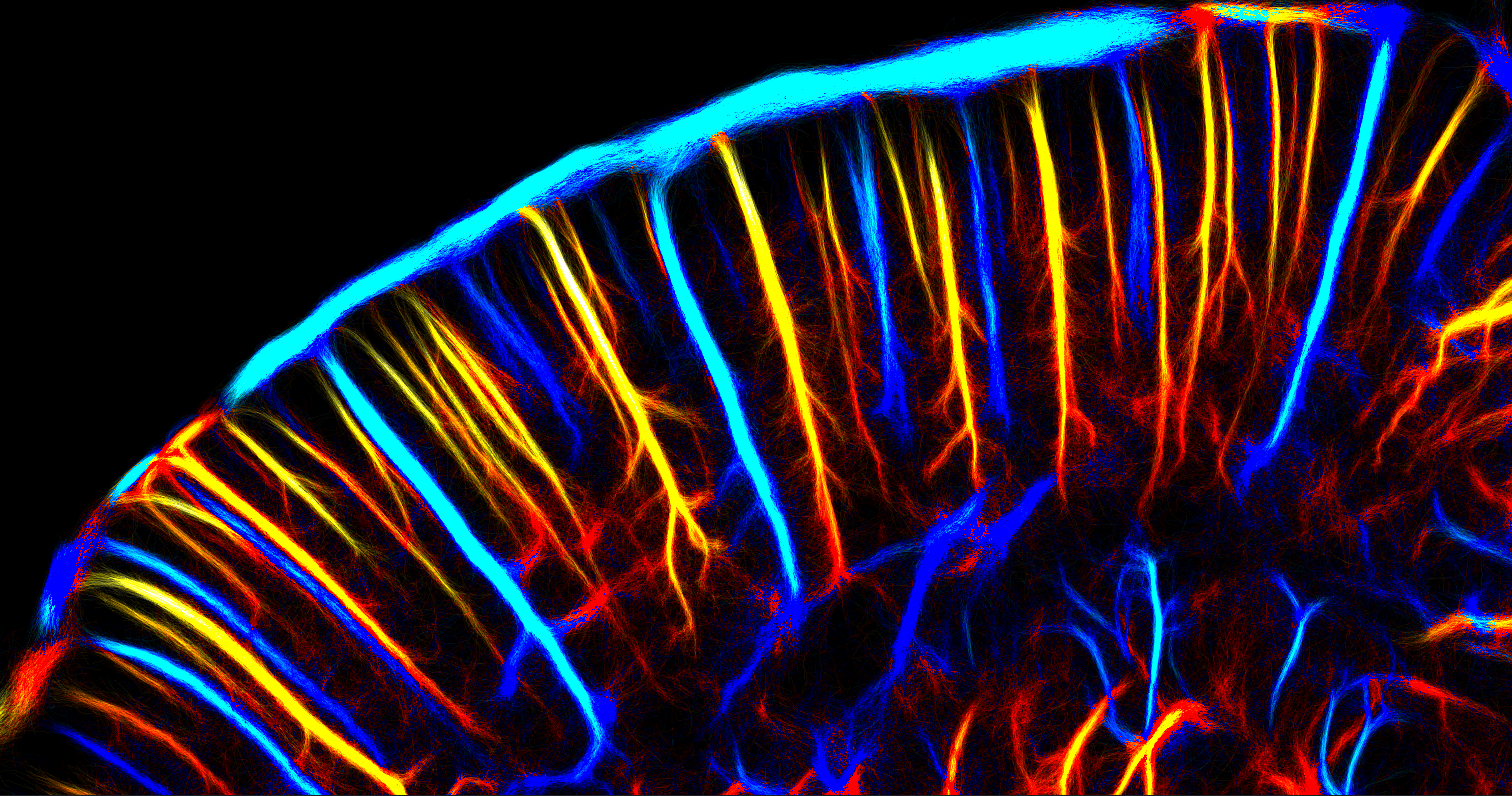
Close-up of the cortex
This parameter allows for discrimination between arterial flow that perfuse the tissues (in red) and venous outflow (in blue).
Credit: Iconeus
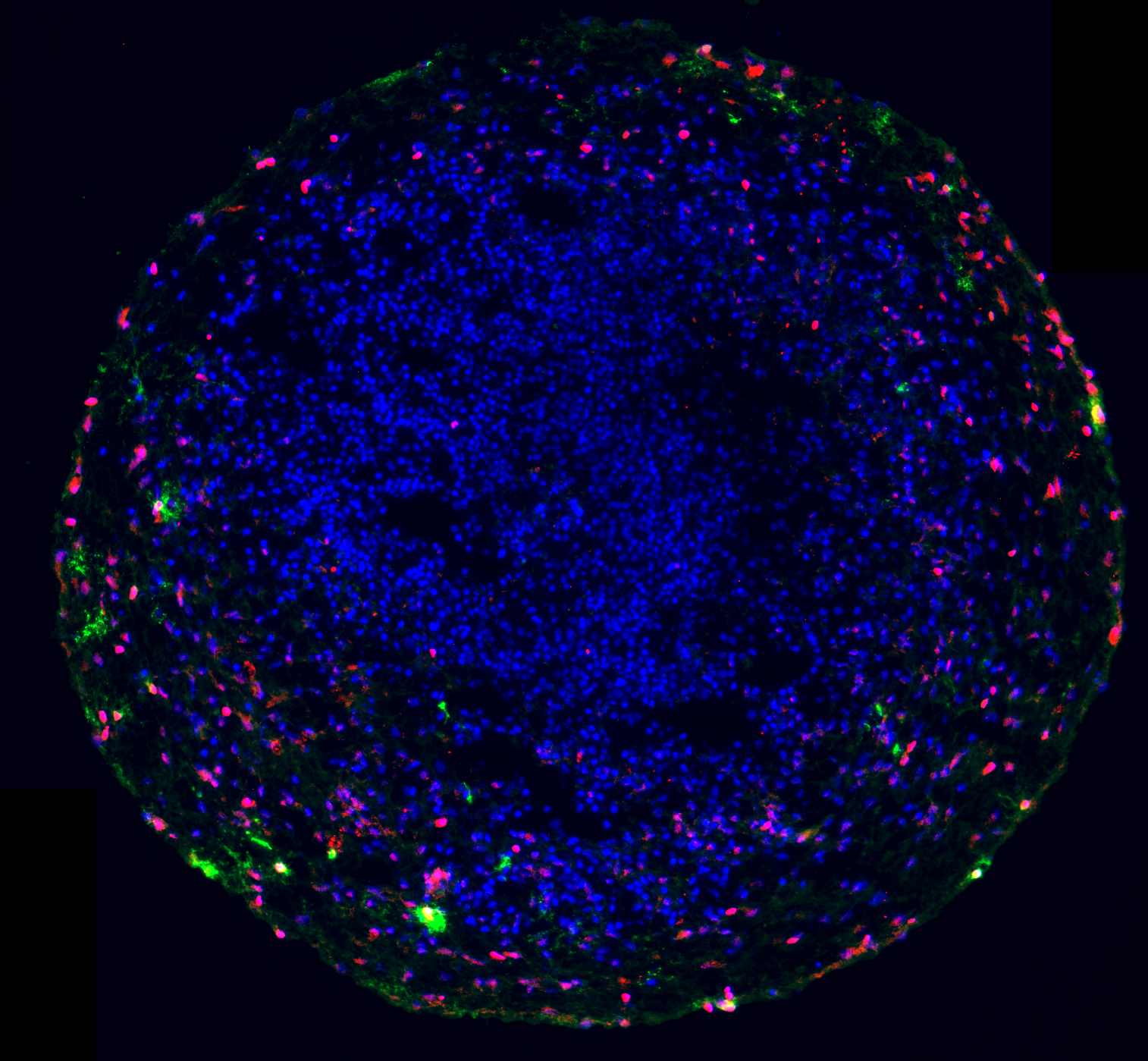
Cortical brain organoid (mini brain)
Organoid cultured from human induced pluripotent stem cells (derived from skin biopsy samples) showing immature (red) and mature (red+green) oligodendrocytes. Mature oligodendrocytes will start to produce myelin in the mini-brain. All cell nuclei are stained in blue.
Credit: Myrna Brandt and Sebastiaan Corstjens, UMC Utrecht
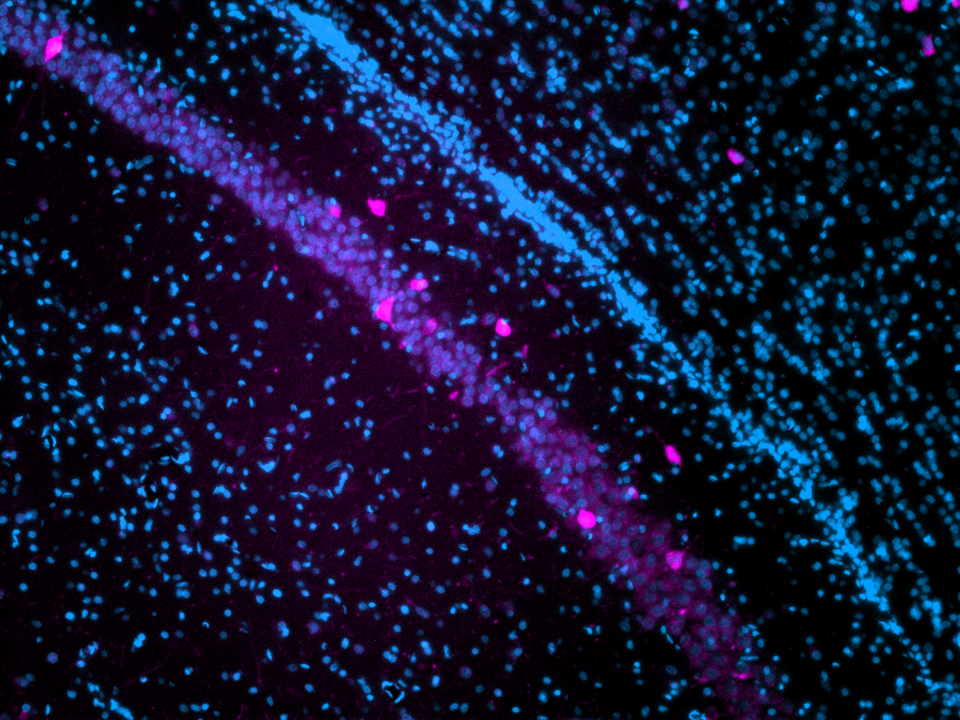
Interneurons in the hippocampus
Parvalbumin-positive interneurons (pink) in the CA2 area of the hippocampus in the rat brain. All cell nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (blue).
Credit: Judit Alhama Riba, UMC Utrecht
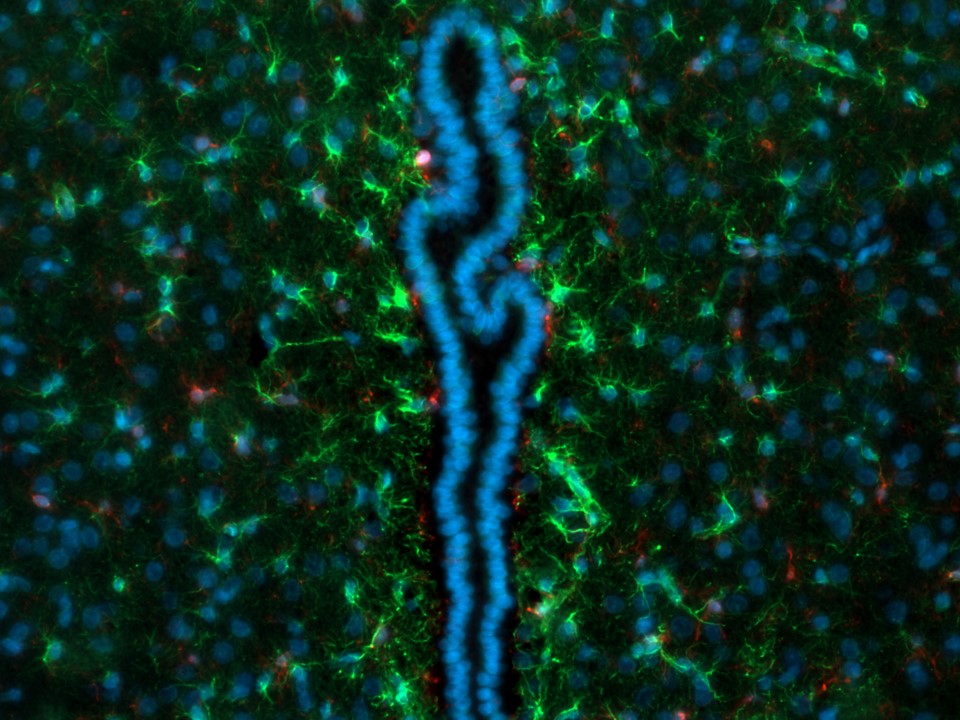
Microglial cells and astrocytes
Microglial cells (red) and astrocytes (green) located at the third ventricle in the rat brain. All cell nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (blue).
Credit: Judit Alhama Riba, UMC Utrecht
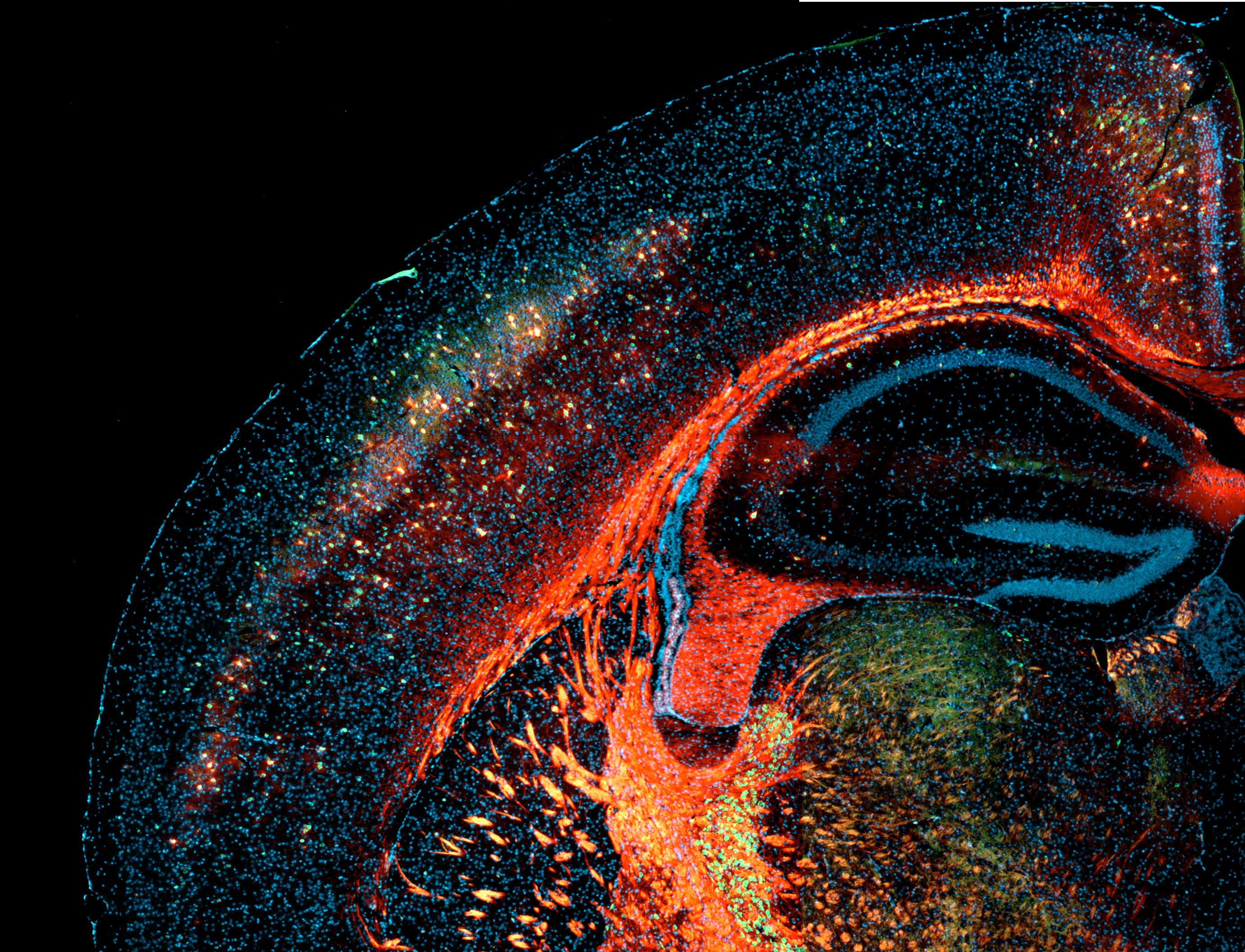
Cortex and hippocampus of the rat brain
Stained in red with N-acetylgalactosamine-binding Wisteria floribunda agglutinin to visualise perineural nets (myelin specifically lights up) and in green for parvalbumin-positive interneurons. Counterstain of all cell nuclei with DAPI in blue.
Credit: Chantal Kosmeijer, UMC Utrecht
More information
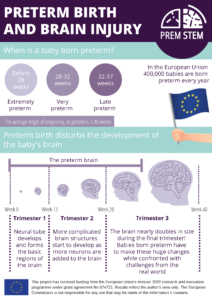
Take a look at our fact sheet on preterm birth and brain injury, available to download in nine languages.
For more brain facts, check out the following websites:
25 Amazing Facts About the Human Brain You Should Probably Memorize